Pibor (river)
| Pibor | ||
|
The river system of the Sobat with the Pibor (middle) |
||
| Data | ||
| location |
|
|
| River system | Nile | |
| Drain over | Sobat → White Nile → Nile → Mediterranean | |
| confluence | of the two rivers Kangen and Veveno at Pibor Post in South Sudan 6 ° 47 ′ 41 ″ N , 33 ° 9 ′ 1 ″ E |
|
| Source height | 417 m | |
| confluence | with the Baro to the Sobat Coordinates: 8 ° 26 ′ 6 ″ N , 33 ° 13 ′ 9 ″ E 8 ° 26 ′ 6 ″ N , 33 ° 13 ′ 9 ″ E |
|
| Mouth height | 404 m | |
| Height difference | 13 m | |
| Bottom slope | 0.04 ‰ | |
| length | 320 km | |
| Catchment area | 109,000 km² | |
| Discharge at the level confluence with the Baro A Eo : 10,900 km² at the mouth |
MQ Mq |
200 m³ / s 18.3 l / (s km²) |
| Right tributaries | Agwai, Akobo , Gilo | |
| Small towns | Pibor | |
|
The Pibor in Pibor Post at high tide |
||
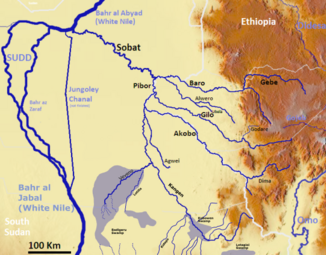
The Pibor is a river in Ethiopia and South Sudan , and a source river of the Sobat .
course
The Pibor has its origin in the place Pibor Post in South Sudan. This is where its source rivers Kangen and Veveno meet. The Kangen rises from the Kobowen Marshes , which are fed by rivers from the border with Kenya and the Ilemi Triangle in the south, and from the Boma Plateau and Boma National Park in the north. The smaller Veveno gets its water from swamps near the city of Bor near the Bahr al-Jabal . In some sources the Kangen is equated with the Pibor.
After Pibor Post, the river flows north. It takes in the rivers Agwai, Akobo and Gilo from the east. From the mouth of the Akobo, the Pibor forms the border with Ethiopia and unites with the Baro around 80 km further to form the Sobat .
Hydrology
The Pibor brings only a good 30 m³ / s of water to the Sobat from the south until shortly before the mouth of the Akobo , a tributary of the Pibor. However, only a few kilometers further east from the Ethiopian highlands, the Akabo already drains almost 90 m³ / s. Accordingly, a good 100 m³ / s flow at the confluence with the Baro, which is about 80 km further in arid and technical areas. In addition there is the runoff of the river Gilo with a further 100 m³ / s. The Baro, also coming from the east, has the highest discharge of 300 m³ / s at the confluence.
Veveno-Pibor Canal
As early as 1934, the implementation of the Veveno-Pibor Canal was published as an alternative to the Jonglei Canal. The aim was to use existing waterways. The plan was to dig a canal from the Bor on the Bahr al-Jabal to the Veveno, a source river of the Pibor, since the Pibor is one of the source rivers of the Sobat, which in turn only flows into the White Nile after the Sudd . However, the project was not implemented.
River history
There are theories, based on sediment analyzes and fauna, that the now endorheic Lake Turkana drained into the Nile catchment area during floods over the Kangen and Pibor until about 7,500 years ago. Thus the catchment area of the Pibor at that time was 146,000 km² larger than today.
Individual evidence
- ^ Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary . Merriam-Webster , 1997, ISBN 0-87779-546-0 , p. 929 . ; online at Google Books
- ^ The Hydrology of the Nile
- ^ A b Hydrologic Regime in the Nile Basin - Mean annual flow of the Nile and main tributaries upstream of Lake Nasser
- ↑ Estimation of Monthly Flow for Ungauged Catchment (Case Study Baro - Akobo basin)
- ↑ The Veveno-Pibor Canal Project Survey (1934)
- ^ Fish Diversity, Community Structure, Feeding Ecology, and Fisheries of LowerOmo River and the Ethiopian Part of Lake Turkana, East Africa
- ↑ The Nile: Origin, environments, limnology and human use (Monographiae Biologicae)
- ^ The Nile Basin: Quaternary Geology, Geomorphology and Prehistoric Environments