Pivalaldehyde
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Pivalaldehyde | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 10 O | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 86.13 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.793 g cm −3 (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
6 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
74 ° C (973 hPa) |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
14.8 kPa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.378 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Pivalaldehyde (also pivalaldehyde ) is a chemical compound from the group of aldehydes . With its isomers valeraldehyde ( n- pentanal), isovaleraldehyde and 2-methylbutyraldehyde , it forms the group of pentanals .
use
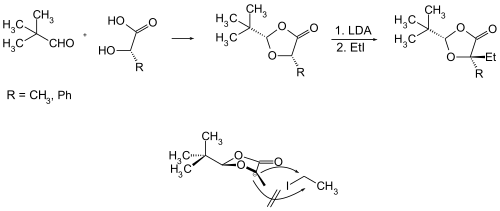
By reacting pivaldehyde with enantiomerically pure lactic acid , mandelic acid or proline , a sterically fixed acetal is obtained which is used in stereoselective synthesis. The α-hydroxycarboxylic acids ( S ) -lactic acid (R = CH 3 ) or ( S ) -mandelic acid (R = C 6 H 5 = Ph) react diastereoselectively as follows:
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Data sheet trimethylacetaldehyde from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on December 1, 2012 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Entry on pivalaldehyde at TCI Europe, accessed on December 2, 2012.
- ↑ Dieter Seebach , Reto Naef: Enantioselective Generation and Diastereoselective Reactions of Chiral Enolates Derived from α-Heterosubstituted Carboxylic Acids , Helvetica Chimica Acta , 1981 , 64 , pp. 2704-2708 ( doi : 10.1002 / hlca.19810640829 ).