Mandelic acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Structure without specifying the stereochemistry | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Mandelic acid | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 8 O 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless crystals |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 152.15 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.30 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
3.37 (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
The mandelic acid (α-hydroxyphenylacetic acid) is a chemical compound from the group of aromatic carboxylic acids .
Isomers
Due to the stereocenter at the α-C atom, mandelic acid forms two enantiomers , D - (-) - and L - (+) - mandelic acid [synonyms: ( R ) - and ( S ) -mandelic acid].
| Isomers of mandelic acid | ||
| Surname | ( R ) -mandelic acid | ( S ) -mandelic acid |
| other names | D - (-) - mandelic acid | L - (+) - mandelic acid |
| Structural formula |
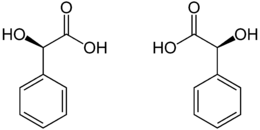
|
|
| CAS number | 611-71-2 | 17199-29-0 |
| 90-64-2 (mixture) | ||
| EC number | 210-276-6 | 241-240-8 |
| 202-007-6 (mixture) | ||
| ECHA info card | 100.009.343 | 100.037.476 |
| 100.001.825 (mixture) | ||
| PubChem | 11914 | 439616 |
| 1292 (mixture) | ||
| DrugBank | - | DB2280 |
| - (mixture) | ||
| Wikidata | Q63390533 | Q27096314 |
| Q412293 (mixture) | ||
Synthesis and manufacture
Mandelic acid was discovered in 1831 by the German pharmacist Ferdinand Ludwig Winckler (1801–1868) when he heated amygdalin , an extract from bitter almonds , with dilute hydrochloric acid . Mandelic acid is obtained industrially from benzaldehyde and hydrocyanic acid in order to be further processed in various medicines.
The biotechnological production of 4-hydroxy-mandelic acid and mandelic acid on the basis of glucose was demonstrated with the help of a genetically modified yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae , whereby the naturally occurring hydroxymandelate synthase in the bacterium Amycolatopsis is incorporated into a wild-type strain of yeast, partially changed by the exchange of a gene sequence and was expressed .
properties
It is a white, crystalline solid.
effect
Mandelic acid has a bacteriostatic or bactericidal effect on streptococci , staphylococci and coli bacteria in an acidic environment .
Too high styrene burdens in the breath values mandelic acid in the urine are reflected in the occupational medical diagnostics (plastic production) as high down.
use
( R ) - or ( S ) -mandelic acid is also used in asymmetric aldol reactions and serves as a chiral ligand. ( R ) -Mandelic acid forms diastereomeric salts with racemic amines, which can often be separated by fractional crystallization. The respective enantiomerically pure amine can then be obtained therefrom by adding a base. With this method, for example, the resolution of the drug ( RS ) - penbutolol has been successful. ( S ) -Mandelic acid can also be used as a reagent for the resolution of racemic amines.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ entry to Mandelic ACID in CosIng database of the European Commission, accessed on 13 August 2020th
- ↑ a b c d Entry on mandelic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on March 29, 2014.
- ^ The Merck Index . An Encyclopaedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals . 14th edition, 2006, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 , p. 989.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Dissociation Constants of Organic Acids and Bases, pp. 8-48.
- ↑ Data sheet mandelic acid at AlfaAesar, accessed on June 7, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Entry on mandelic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on Mandelic acid in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), accessed on January 11, 2020.
- ↑ Mara Reifenrath, Eckhard Boles: Engineering of hydroxymandelate synthases and the aromatic amino acid pathway enables de novo biosynthesis of mandelic and 4-hydroxymandelic acid with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metabolic Engineering January 45, 2018; Pp. 246-254. doi : 10.1016 / j.ymben.2018.01.001 .
- ↑ AWMF online work under the influence of benzene, its homologues or styrene ( Memento from September 30, 2007 in the Internet Archive ).
- ↑ Rainer Mahrwald: Titanium (IV) alkoxides Ligand Exchange with α-Hydroxy Acids: The Enantioselective aldol addition. In: Organic Letters. 2, 2000, pp. 4011-4012, doi : 10.1021 / ol0002727 .
- ↑ Hermann J. Roth , Christa E. Müller and Gerd Folkers: Stereochemie & Arzneimittel, Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft Stuttgart, 1998, ISBN 3-8047-1485-4 , pp. 164-165.
