Polybutene
| Structural formula | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
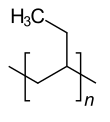
|
|||||||
| General | |||||||
| Surname | Polybutene | ||||||
| other names |
|
||||||
| CAS number | 9003-28-5 | ||||||
| Monomer | 1-butene | ||||||
| Molecular formula of the repeating unit | C 4 H 8 | ||||||
| Molar mass of the repeating unit | 56.11 g mol −1 | ||||||
| Type of polymer | |||||||
| Brief description |
Polyolefin with good creep strength and chemical resistance |
||||||
| properties | |||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||
| Melting point |
124-126 ° C |
||||||
| Crystallinity |
partially crystalline |
||||||
| modulus of elasticity |
290-295 MPa |
||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||
|
|||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||
Polybutene , also called polybutylene ( abbreviation PB ), is a thermoplastic polyolefin . In contrast to the branched polyisobutylene , the monomers in PB are arranged linearly and largely isotactically , with overall high molar masses of 700,000 to 3,000,000 g / mol being achieved.
Synthesis and processing
The polymerization of PB takes place with the help of specific Ziegler-Natta catalysts . When it cools, about half of the polymer crystallizes tetragonally, resulting in a soft and rubbery material. The density is then around 890 kg · m −3 . Under pressure or with further cooling, shrinkage occurs, since the tetragonal phase changes into a hexagonal phase. The density (to approx. 950 kg · m −3 ), strength and hardness increase.
Polybutene can be processed thermoplastically by injection molding or extrusion at temperatures above 190 ° C. To ensure quick demolding, the mold temperatures are only around 40 to 80 ° C during injection molding.
properties
In terms of mechanical properties, PB is roughly between PE and PP . Due to its high molar mass, it has good temperature resistance, which is evident, for example, in its high creep strength (or low tendency to creep ). PB also has good chemical resistance to many solvents, oils , fats , acids , alkalis , hot water , alcohols and ketones . In addition, it is harmless in contact with food. Compared to some engineering plastics, it is less resistant to aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons and oxidizing acids.
Like all polyolefins, PB is also highly flammable and not weather-resistant without additional stabilization.
Applications
Typical fields of application for PB are pipelines and, together with PE and PP films, for food packaging . PB is also a component in many hot melt adhesives or is added to other polyolefins as a processing aid in blends .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Saechtling , Kunststoff-Taschenbuch, 29th edition 2004, ISBN 3-446-40352-3 .
- ↑ a b c d Andrew Freeman, Susan C. Mantell, Jane H. Davidson: Mechanical performance of polysulfone, polybutylene, and polyamide 6/6 in hot chlorinated water . In: Solar Energy . 79, No. 6, 2005, pp. 624-37. doi : 10.1016 / j.solener.2005.07.003 .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.