Polyisobutylene
| Structural formula | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||
| General | |||||||
| Surname | Polyisobutylene | ||||||
| other names |
PIB, polyisobutene |
||||||
| CAS number | 9003-27-4 | ||||||
| Monomer | Isobutene | ||||||
| Molecular formula of the repeating unit | C 4 H 8 | ||||||
| Molar mass of the repeating unit | 56.11 g mol −1 | ||||||
| Type of polymer | |||||||
| properties | |||||||
| Physical state |
liquid to solid |
||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||
|
|||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||
Polyisobutene or polyisobutylene ( abbreviation : PIB ) was first produced in 1931 by the Badische Anilin- und Sodafabrik ( BASF SE ) in Ludwigshafen-Oppau and marketed under the trade name Oppanol .
Extraction and presentation
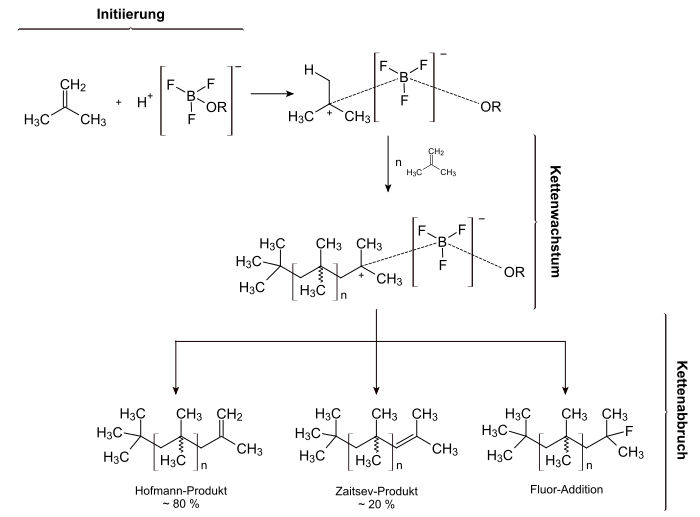
Polyisobutene is synthesized via the cationic polymerization of isobutene (2-methylpropene). The temperature of the reaction is between −100 ° C and 0 ° C, depending on which molar mass range is sought. The lower the reaction temperature, the higher the molar mass of the polymer . The initiators used are Lewis acids such. B. boron trifluoride or aluminum trichloride in conjunction with water or alcohols .
properties
Depending on the degree of polymerization or molar mass, the spectrum of the PIB ranges from a viscous oil (molar mass approx. 300–3000 g · mol −1 ) to plastic sticky masses (molar mass approx. 40,000–120,000 g · mol −1 ) to rubber-like products ( Molar mass approx. 300,000–2,500,000 g · mol −1 )
Since even higher molecular weight PIB is to a certain extent present as a highly viscous liquid at room temperature ( ≤ −60 ° C), it has a certain tendency to creep , which depends on the molar mass; this can be done by adding z. B. talc , carbon black and PE-LD reduced or adjusted with 2,4,4-trimethylpent-1-en (α-diisobutylene). Further properties are:
- low density
- high elongation at break
- Temperature resistance from −30 ° C to +65 ° C (permanent) or +80 ° C (short-term)
- a specific electrical resistance of 10 14 Ωm
- resistant to acids , alkalis , salts and conditionally resistant to nitric acid
- not resistant to chlorine , bromine and chlorosulphonic acid as well as UV radiation ( soot , titanium dioxide and light protection agents act as UV stabilizers)
- swells in aliphatic and aromatic chlorinated hydrocarbons
Polyisobutylene (PIB) should not be confused with the elastomer butyl rubber (IIR), to which it is, however, closely related.
use
PIB can be processed into solutions and dispersions for coating . In addition, like rubber , it can be processed on rolling mills, in kneaders, presses, by calendering and extruding . The processing temperature is between 150 ° C and 240 ° C.
Further applications are sealing compounds , wax admixtures for lamination and coating, plaster adhesives and spray plasters, insect glue on yellow boards , raw material for the production of chewing gum , roof waterproofing membranes, mixtures with polyolefins to improve processability and the plasticization of explosives such as PETN or Hexogen . Polyisobutylene is also used as an additive in other plastics , e.g. B. in butyl rubber mixtures and as a lubricant additive. It is not suitable for cosmetics.
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ a b c Entry on polyisobutenes. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 2, 2014.