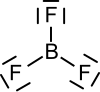
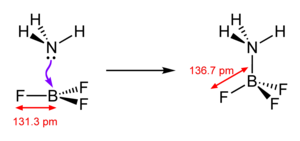Boron trifluoride
| Structural formula | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||
| Surname | Boron trifluoride | ||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||
| Molecular formula | BF 3 | ||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, pungent smelling gas that smokes in moist air |
||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||
| Molar mass | 67.81 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||
| Physical state |
gaseous |
||||||||||
| density |
|
||||||||||
| Melting point |
−127.1 ° C |
||||||||||
| boiling point |
−100.4 ° C |
||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
28 bar (at −30 ° C) |
||||||||||
| solubility |
reacts violently with water |
||||||||||
| Dipole moment |
0 |
||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.316 (20 ° C, dihydrate) |
||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| MAK |
|
||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | |||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−1136.0 (8) kJ / mol |
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||
Boron trifluoride is a chemical compound consisting of the elements boron and fluorine . It has the empirical formula BF 3 and is sometimes referred to as trifluoroborane .
Extraction and presentation
Boron trifluoride can be obtained by:
- Reaction of boron trioxide with hydrofluoric acid :
- on an industrial scale by heating diboron trioxide or borax with calcium fluoride and concentrated sulfuric acid
- in the laboratory by thermolysis of diazonium tetrafluoroborates
- further from sodium or ammonium tetrafluoroborate with boron trioxide in sulfuric acid
- or from fluorosulfonic acid and boric acid :
properties
Boron trifluoride forms a trigonal-planar molecular structure . It is a very toxic chemical compound, which is gaseous at room temperature and has a critical temperature of −12.3 ° C.
Boron trifluoride is a very strong Lewis acid (electron pair acceptor). It forms addition compounds (Lewis acid-base adducts) with electron pair donors .
It reacts with water and decomposes to form boric acid and hydrofluoric acid . In contrast to the other boron trihalides, there is no direct hydrolysis , but a series of several reactions. In this forms due to the strong BF 3 bond firstly a Lewis acid-base - adduct .
However, in contrast to other boron halides, the hydrolysis is not complete, since the inert , tetrahedral tetrafluoroborate (BF 4 - ) is also formed.
The products of hydrolysis also react further to form tetrafluoroboric acid , which is present as the oxonium salt .
use
In the chemical industry, boron trifluoride can be used as a catalyst for a large number of chemical reactions or as a starting material for the production of various boron compounds. Gaseous boron trifluoride and boron trifluoride adducts are mainly used as catalysts or co-catalysts, for example in the production of polymers , high-quality lubricating oils , pharmaceuticals , aromas and fragrances and other fine chemicals as well as for the synthesis of boron compounds such as alkyl boranes , amine boranes and reagents for the Suzuki clutch . It is also used in the semiconductor industry as a source of boron for ion implantation (p-doping), for surface treatment of steel and glass and in neutron detectors.
safety instructions
Boron trifluoride is very toxic and extremely corrosive.
Important BF 3 adducts
- BF 3 - methanol
- BF 3 - phenol
- BF 3 - dibutyl ether
- BF 3 diethyl etherate
- BF 3 - dimethyl ether
- BF 3 -THF ( tetrahydrofuran )
- BF 3 - acetic acid
- BF 3 - acetonitrile
- BF 3 dihydrate
- BF 3 - phosphoric acid
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on boron trifluoride. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on January 17, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet boron trifluoride from AlfaAesar, accessed on February 22, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) . .
- ↑ a b data sheet Boron trifluoride dihydrate, 96% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 8, 2014 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c Entry on boron trifluoride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Gases, pp. 6-188.
- ↑ Entry on boron trifluoride in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for boron trifluoride ), accessed on March 4, 2020.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, CODATA Key Values for Thermodynamics, pp. 5-1.
- ↑ HS Booth and KS Willson: Boron trifluoride . In: Harold Simmons Booth (Ed.): Inorganic Syntheses . tape 1 . McGraw-Hill, Inc., 1939, p. 21-24 (English).
- ↑ Georg Brauer (Ed.): Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 2nd edition. Volume 1. Academic Press, New York NY et al. 1963, pp. 219-221.








![{\ mathrm {H_ {2} O ^ {{+ -}} BF_ {3} + H_ {2} O \ \ rightleftharpoons \ [H_ {3} O] [BF_ {3} OH]}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/85038085d3a220e22a7c1b738bdc70bddc160e09)
![{\ mathrm {[H_ {3} O] [BF_ {3} OH] + H_ {2} O \ \ rightleftharpoons \ B (OH) _ {3} +3 \ HF}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/19d0d18e7c28efd174dd7b6b3e7ed59a28687277)

![{\ mathrm {B (OH) _ {3} +4 \ HF \ \ rightleftharpoons \ [H_ {3} O] [BF_ {4}] + 2 \ H_ {2} O}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8ba8cb6f1d01ef57537efd097c2be25721e03d9c)