Butene
Butenes (also butylenes ) are a group of four isomeric hydrocarbons with the general empirical formula C 4 H 8 , which have a C = C double bond . They are therefore one of the alkenes . Two of the isomers differ in their cis - trans isomerism .
Butenes are colorless, flammable gases with a greater density than air under standard conditions . The isomers can be liquefied under pressure. In higher concentrations they have a narcotic and suffocating effect. They form explosive mixtures with air.
Structure and properties
| Properties of butenes | ||||||||||||
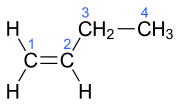
| Surname | 1-butene | ( Z ) -But-2-ene | ( E ) -But-2-ene | 2-methylprop-1-en | ||||||||
| other names | 1-butene n -butene 1-butylene α-butylene |
cis -2-butene ( Z ) -2-butene cis -but-2-ene |
trans -2-butene ( E ) -2-butene, trans -but-2-ene |
2-methyl-1-propene isobutene i- butylene |
||||||||
| structure |
|
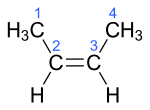
|

|
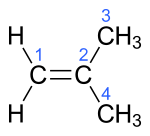
|
||||||||
| CAS number | 106-98-9 | 590-18-1 | 624-64-6 | 115-11-7 | ||||||||
| CAS number isomer mixture | 25167-67-3 | |||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 8 | |||||||||||
| Molar mass | 56.11 g mol −1 | |||||||||||
| Brief description | colorless gases | |||||||||||
| Melting point | −185.4 ° C | −138.9 ° C | −105.5 ° C | −140.4 ° C | ||||||||
| boiling point | −6.2 ° C | 3.7 ° C | 0.9 ° C | −7.1 ° C | ||||||||
| Heat of evaporation at the boiling point | 22.07 kJ mol −1 | 23.34 kJ mol −1 | 22.72 kJ mol −1 | 24.03 kJ mol −1 | ||||||||
| Vapor pressure | 2.545 bar (20 ° C) | 1.813 bar (20 ° C) | 1.991 bar (20 ° C) | 2.59 bar (20 ° C) | ||||||||
| Lower explosion limit (20 ° C / 1.013 bar) | 1.2% by volume / 28 g m 3 | 1.6% by volume / 37 g m 3 | 1.6% by volume / 37 g m 3 | 1.6% by volume / 37 g m 3 | ||||||||
| Upper explosion limit (20 ° C / 1.013 bar) | 10.6% by volume / 252 g m 3 | 10.0% by volume / 235 g m 3 | 10.0% by volume / 235 g m 3 | 10.0% by volume / 235 g m 3 | ||||||||
| Ignition temperature / temperature class | 360 ° C / T2 | 324 ° C / T2 ( E / Z -isomer mixture) | 324 ° C / T2 ( E / Z -isomer mixture) | 465 ° C / T1 | ||||||||
| solubility | practically insoluble in water, easily soluble in ethanol and ether | |||||||||||
|
GHS labeling |
from Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP) , expanded if necessary
|
from Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP) , expanded if necessary
|
from Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP) , expanded if necessary
|
from Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP) , expanded if necessary
|
||||||||
| H-phrases | 220-280 | 220 | 220 | 220-280 | ||||||||
| EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | |||||||||||
| P-phrases | 210-377-381-403 | 210 | 210 | 210-377-381-403 | ||||||||
Thermodynamic properties
Butenes are gases that are easy to liquefy and their application and conversion often take place under increased pressure as a liquid or in a supercritical state.
| Vapor-liquid equilibria | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surname | 1-butene | ( Z ) -But-2-ene | ( E ) -But-2-ene | 2-methylprop-1-en |
| Vapor pressure function after Antoine | Parameters according to log 10 (P) = A− (B / (T + C)) (P in bar, T in K) | |||
| A. | 4.24696 | 3,98744 | 4.04360 | 3.64709 |
| B. | 1099.207 | 957.060 | 982.166 | 799.055 |
| C. | −8.265 | −36.504 | −30.775 | −46.615 |
| Temperature range | 195.6K - 269.4K | 203.06K - 295.91K | 201.70K - 274.13K | 216.40K - 273K |
| source | ||||
| Critical sizes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surname | 1-butene | ( Z ) -But-2-ene | ( E ) -But-2-ene | 2-methylprop-1-en |
| Critical temperature T c | 146.35 ° C / 419.5 K | 162.35 ° C / 435.5 K | 155.45 ° C / 428.6 K | 144.75 ° C / 417.9 K |
| Critical pressure p c | 40.2 bar | 42.1 bar | 41.0 bar | 40.0 bar |
| Critical molar volume V m, c | 0.2408 l mol −1 | 0.2338 l mol −1 | 0.2377 l mol −1 | 0.2388 l mol −1 |
| Critical density ρ c | 4.15 mol·l −1 | 4.28 mol·l −1 | 4.21 mol·l −1 | 4.19 mol·l −1 |
synthesis
Michael Faraday found butene in 1825 as a gaseous component in the distillation of crude oil (see also: liquid gas ). Butenes can be obtained as a mixture of isomers by cracking petroleum. They are also obtained through the catalytic dehydrogenation of n-butane or isobutane . The isomers can be separated with the aid of zeolites .
use
The CC double bond makes them interesting and important starting materials for chemical syntheses . They are used to produce compounds such as 2-butanol , 2-butanone (ethyl methyl ketone) and 1,3-butadiene and are the starting material for the production of plastics (e.g. butyl rubber and polyisobutene ). As alkylating agents they are used, for. B. for the synthesis of additives for knock-resistant fuels ( 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (isooctane)). Isobutene is required for the synthesis of methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) or ethyl tert-butyl ether (ETBE). Also tert -butyl ester can be produced acids via the reaction of isobutene and (carbon). This synthesis route is particularly suitable if, in the esterification with tert- butanol as a competing reaction , its dehydration dominates.
literature
- FMA horny; G. Stochniol; S. Peitz; E. Schulte-Körne: butenes , in: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry , Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2013; doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a04_483.pub3 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on butene, mixture of isomers in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on October 23, 2013(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on 1-butene in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on August 11, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on cis-2-butene in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on August 11, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on trans-2-butene in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on August 11, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on 2-methylpropene in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on August 11, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ^ A b c V. Majer, V. Svoboda: Enthalpies of Vaporization of Organic Compounds: A Critical Review and Data Compilation. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford 1985, p. 300.
- ↑ RC Weast (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 66th edition. CRC Press, 1985, ISBN 0-8493-0466-0 .
- ↑ a b c E. Brandes, W. Möller: Safety-related parameters. Volume 1: Flammable Liquids and Gases. Wirtschaftsverlag NW - Verlag für neue Wissenschaft, Bremerhaven 2003.
- ↑ a b c d Entry on Butene. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 25, 2019.
- ↑ Entry on But-1-ene in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 11, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Entry on (Z) -but-2-ene in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 11, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Entry on (E) -but-2-ene in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 11, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Entry on 2-methylpropene in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 11, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ^ CC Coffin, O. Maass: The Preparation and Physical Properties of "alpha", "beta" and "gamma" -Butylene and Normal and Isobutane. In: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 50, 1928, pp. 1427-1437.
- ^ RB Scott, WJ Ferguson, FG Brickwedde: Thermodynamic properties of cis-2-butene from 15 ° to 1,500 K. In: J. Res. NBS . 33, 1944, pp. 1-20.
- ↑ L. Guttman, KS Pitzer: trans-2-butenes. The heat capacity, heats of fusion and vaporization, and vapor pressure. The entropy and barrier to internal rotation. In: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 67, 1945, pp. 324-327.
- ^ AB Lamb, EW Roper: The Vapor Pressures of Certain Unsaturated Hydrocarbons. In: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 62, 1940, pp. 806-814.
- ↑ C. Tsonopoulos, D. Ambrose: Vapor-Liquid Critical Properties of Elements and Compounds. 6. Unsaturated Aliphatic Hydrocarbons. In: J. Chem. Eng. Data . 41, 1996, pp. 645-656.

