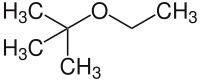
ETBE
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Ethyl tert -butyl ether | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 14 O | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 102.18 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.74 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−94 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
73 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
173 hPa (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.375 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data |
> 2000 mg / kg ( LD 50 , rabbit , transdermal ) |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
| ETBE | |
|---|---|
| Brief description | Anti-knock agents for petrol |
| properties | |
| Physical state | liquid |
| Octane number |
117 RON, 101 MOZ |
| Flash point |
−19 ° C |
| Explosive limit | 1.2-7.7% by volume |
| safety instructions | |
| UN number | 1179 |
| Hazard number | 33 |
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |
ETBE (according to IUPAC nomenclature: 2-ethoxy-2-methylpropane , also written out as ethyl tert -butyl ether ) is an organic-chemical compound from the group of aliphatic ethers . On the one hand, because of its use as an anti-knock agent in petrol and, on the other hand, as a solvent in organic chemistry, it has acquired a certain industrial importance.
Extraction and presentation
Industrial synthesis
Ethyl tert -butyl ether is industrially produced by acid-catalyzed etherification of isobutene with ethanol at temperatures of 30 - 13 bar at - 110 ° C and pressures of 8 acidic ion exchange resins prepared.
As reactors for this purpose are especially suitable fixed-bed reactors , such as tube-bundle or circulatory reactors in which the reverse current can be cooled optional.
Laboratory synthesis
In the laboratory, ethyl tert-butyl ether can also be produced by the acid-catalyzed etherification of tert-butanol with ethanol at 40 ° C. 15% strength aqueous sulfuric acid is used as the catalyst .
The desired ethyl tert-butyl ether is obtained in 95% yield . This is due to the thermodynamic stability of the tertiary carbenium ion formed as an intermediate . For this reason, the competing condensation reaction of two ethanol molecules to form diethyl ether is kept very low.
properties
Physical Properties
Ethyl tert -butyl ether has a relative gas density of 3.53 (density ratio to dry air at the same temperature ) and a density of 0.74 g / cm 3 at 20 ° C. In addition, ETBE has a vapor pressure of 173 hPa at 25 ° C.
Chemical properties
Ethyl tert -butyl ether is a flammable liquid from the substance group of the ether . It is lighter than water and not very soluble in it (12 g / l at 25 ° C). In return, it has very good solubility in ethanol and diethyl ether. The volatile ethyl tert-butyl ether can easily form peroxides with air . Therefore, explosive vapor-air mixtures can arise.
use
ETBE is added to petrol in a similar way to methyl tert -butyl ether (MTBE) or tert- amyl ethyl ether (TAEE) to improve the knock resistance (maximum 15% by volume). MTBE is produced from fossil raw materials. ETBE, however, can e.g. B. from fossil isobutene and ethanol from renewable raw materials ( bioethanol ).
In the EU , according to the Renewable Energy Sources Directive (EC), 10% renewable energies must be used in the transport sector by 2020. Much of this goal is to be achieved through the use of biofuels. In Germany, the Biofuel Quota Act (BioKraftQuG) stipulated a minimum share of biofuels of 8% (energetic) in the entire fuel market until 2015. This was reduced again by the law amending the promotion of biofuels , so that a biofuel quota of 6.25% will apply until 2014. Due to the stoichiometrically calculated bioethanol content in "Bio-ETBE", 47% of this can be assessed as a biofuel admixture. ETBE is more expensive than bioethanol. It is therefore only mixed with petrol if, for technical reasons (e.g. lack of admixture technology), bioethanol cannot be used or if higher-quality petrol variants are to be produced. The octane number of ETBE (117) is higher than that of ethanol (104).
As part of the MTBE ban (see MTBE ), adding ETBE to motor gasoline is also prohibited in a number of US states.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Entry on ethyl tert-butyl ether in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on March 8, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 88th edition. (Internet version: 2008), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-80. .
- ↑ Data sheet tert-butyl ethyl ether from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 20, 2015 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b François GARIN: FORMULATIONS OF FUELS ( Memento of 15 October 2005 at the Internet Archive ) (PPT).
- ↑ a b Matthias Grömping, Frank Höper, Jörg Leistner, Franz Nierlich, Udo Peters, Jochen Praefke, Armin Rix, Dirk Röttger, Silvia Santiago Fernandez: Process for the production of ethyl tert-butyl ether from technical mixtures of C4 hydrocarbons. In: Google Patents. EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH, July 12, 2007, accessed on February 21, 2019 .
- ^ A b K. Peter C. Vollhardt, Neil E. Schore: Organic chemistry . Ed .: Holger Butenschön. 5th edition. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim / Germany 2011, ISBN 978-3-527-32754-6 , p. 390 .
- ↑ Environmental Protection Agency , USA: Gasoline Composition Regulations Affecting LUST Sites (PDF; 1.1 MB).



