Pravastatin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
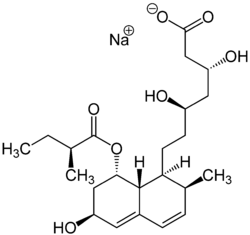
|
|||||||||||||
| Pravastatin sodium salt | |||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Pravastatin | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 23 H 36 O 7 | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid (sodium salt) |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | |||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 424.53 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in methanol and water, slightly soluble in isopropanol, practically insoluble in acetone, acetonitrile, chloroform and ether |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Pravastatin is a chiral drug from the group of statins , used in the treatment of high cholesterol levels is used. It is taken to prevent cardiovascular complications as long as there is no coronary artery disease.
The natural substance pravastatin is one of the monacolines and is obtained from Nocardia autotrophica (as well as Syncephalastrum nigricans , Absidia coerulea ). Pravastatin was 1991 after lovastatin and simvastatin as a third HMG-CoA reductase - inhibitor ( statin ) in the trade.
Mechanism of action
Pravastatin is a competitive HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. The HMG-CoA reductase acts as a catalyst in the reduction of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A to mevalonate, which is a limiting step in the hepatic cholesterol synthesis. By lowering the cholesterol synthesis, the liver cells increase the number of LDL receptors on the cell surface, so that the LDL uptake into the liver cell increases and thus the LDL level in the blood is reduced.
Side effects
Pravastatin can u. a. Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhea, constipation, flatulence), fatigue, muscle pain and headache and joint pain.
Stereoisomerism
Pravastatin contains eight stereogenic centers. So there are theoretically 256 stereoisomers . Only a clearly defined stereoisomer (see formula) in the form of the sodium salt is used as a medicinal substance .
Trade names
Mevalotin (D, CH), Panchol (A), Pravagamma (D), Pravalip (D), Pravalotin (CH), Pravasin protect (D), Pravasta (CH), Pravastax (CH), Pravatin (CH), Selipran ( CH), Statinoprav (A), numerous generics (D, A, CH)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Data sheet Pravastatin, Sodium Salt (PDF) from Calbiochem, accessed on December 8, 2015.
- ^ The Merck Index . An Encyclopaedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals . 14th edition, 2006, p. 1325, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 .
- ↑ Data pravastatin sodium salt hydrate at Sigma-Aldrich accessed on 22 April 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b entry on pravastatin. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 28, 2014.
- ^ Kurt Langbein, Hans-Peter Martin, Hans Weiss: Bitter Pills . 78th edition. Kiepenheuer & Witsch, 2008, ISBN 978-3-462-04004-3 , p. 695.
- ↑ Red List online, as of September 2009.
- ↑ AM comp. d. Switzerland, as of September 2009.
- ↑ AGES-PharmMed, as of September 2009.