Silver hexafluoroantimonate (V)
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| __ Ag + __ Sb 5+ __ F - | |||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
cubic |
||||||||||||||||||
| Space group |
Ia 3 (No. 206) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Lattice parameters |
a = ?? 979.85 (4) pm, Z = 8 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Coordination numbers |
[8] Ag, [6] Sb |
||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Silver (I) -hexafluoroantimonate (V) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | Ag [SbF 6 ] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
beige powder |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 343.62 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Silver hexafluoroantimonate , Ag [SbF 6 ] is a chemical compound between silver and hexafluoroantimonic acid .
properties
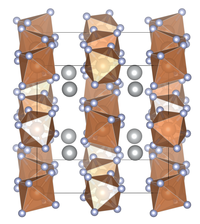
Silver hexafluoroantimonate is a beige powder. It is soluble in water. At room temperature the compound crystallizes in the cubic space group Ia 3 (space group no. 206) in a structure similar to the cesium chloride type. The lattice constants are a = ?? 979.85 (4) pm and Z = 8.
use
Silver hexafluoroantimonate can be used as a catalyst.
safety instructions
In oral ingestion or inhalation , the compound is toxic. The eyes can become irritated. Symptoms after exposure to silver hexafluoroantimonate are inflammation and edema of the larynx as well as the bronchi and lungs . Nausea and headache are other signs.
Strong oxidizing agents can react violently with the salt. During the decomposition, hydrogen fluoride and antimony oxides can be released.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Kazuhiko Matsumotoa, Rika Hagiwaraa, Yasuhiko Itoa, Osamu Tamada: Crystal structures of AgAF 6 (A = P, As, Sb, Nb, Ta) at ambient temperatures . In: Journal of Fluorine Chemistry . tape 110 , no. 2 , August 2001, p. 117-122 , doi : 10.1016 / S0022-1139 (01) 00418-3 .
- ↑ a b c d data sheet Silver hexafluoroantimonate (V) from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 16, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet Silver (I) hexafluoroantimonate at AlfaAesar, accessed on February 16, 2019 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ^ Mathieu Bui The Thuong, André Mann, Alain Wagner: Mild chemo-selective hydration of terminal alkynes catalysed by AgSbF6. In: Chem. Commun. 48, 2012, p. 434, doi : 10.1039 / C1CC12928G .
- ↑ Ian Fairlamb, Jason Lynam: Organometallic Chemistry . Royal Society of Chemistry, 2015, ISBN 978-1-84973-984-9 , pp. 62 ( limited preview in Google Book search).


