L-ribonucleic acid aptamer
L -Ribonukleinsäureaptamere (short L -RNA aptamers ) are ribonucleic acid (RNA) related molecules consisting of unnatural L - ribonucleotides are constructed. They are artificial oligonucleotides and stereochemical mirror images of natural oligonucleotides. L- ribonucleic acid aptamers represent a special form of aptamers and, like them, canbindspecific molecules, for example proteins , via their three-dimensional structure. Thanks to the use of L nucleotides, they are characterized by high enzymatic stability. L- ribonucleic acid aptamers are currently beingdevelopedas potential medicinal products under the brand name Spiegelmer (from Greek meros 'area' )and are beingtestedin clinical studies .
properties
Chemical properties
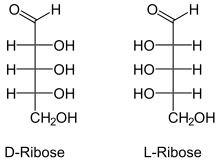
L -ribonucleic acid aptamers are built up from L -nucleotides as the stereochemical mirror images ( enantiomers ) of natural oligonucleotides . Nucleotides from which amptamers including L- ribonucleic acid aptamers are built, i.e. adenosine monophosphate (AMP), guanosine monophosphate (GMP), cytidine monophosphate (CMT) and uridine monophosphate (UMP), consist of a phosphate residue , a nucleobase and a ribose group as a carrier of the chiral center . By exchanging the natural D -ribose for its enantiomer, the artificial L -ribose, L -nucleotides are created, the building blocks of the L -ribonucleic acid aptamers.
Biological properties
Like other aptamers, L- ribonucleic acid aptamers are able to bind molecules such as peptides , proteins and low molecular weight substances. The affinity of L- ribonucleic acid aptamers for their target molecules is often in the picomolar to nanomolar range and is therefore comparable to that of antibodies . L- ribonucleic acid aptamers themselves have a low antigenicity. In contrast to other aptamers, which can be hydrolytically split by enzymes , L- ribonucleic acid aptamers have a high stability in the blood serum . Regardless of this, due to their low molar mass , which is below the renal threshold , they are excreted via the kidneys within a short time . Modified L- ribonucleic acid aptamers with a higher molar mass, for example pegylated spiegelmers, show a prolonged plasma half-life .
Manufacturing
In contrast to other aptamers, L -ribonucleic acid aptamers can not be obtained using the conventional technique known as systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX), since L- nucleic acids cannot be amplified using enzymatic processes such as the polymerase chain reaction. Therefore, the selection takes place via the detour of conventional D- nucleic acids using mirrored target molecules.
1. Reflection of the target molecule
In the first step, a mirror image of the target molecule is artificially created. In the case of peptides and smaller proteins, these are produced synthetically using artificial D -amino acids, the enantiomers of the natural amino acids, with the aid of peptide synthesis . If the target molecule is a larger protein, the mirror image of an epitope can optionally be produced with the aid of peptide synthesis using D- amino acids.
2. SELEX
A conventional molecule library consisting of up to 10 16 different oligonucleotides serves as the starting point for the subsequent SELEX process. In cycles of selection using the mirror image of the target molecule, separation, amplification and possibly mutation, the oligonucleotides that bind the mirror image of the target molecule best are isolated.
3. Sequencing and Synthesis
With the help of DNA sequencing , the nucleic acid sequence of the oligonucleotides obtained from the SELEX process is determined. This information is used for the artificial synthesis of the mirror image of the oligonucleotide, the Spiegelmer, using L nucleotides.
use
L- ribonucleic acid aptamers, which are directed against the chemokines CCL2 and CXCL12 , the complement component C5a and ghrelin , for example , represent potential drugs. They are currently in preclinical or clinical development. To date, three L- ribonucleic acid aptamers have completed clinical phase IIa studies. These include the anti-CCL2- L -Ribonukleinsäureaptamer Emapticap , the anti-CXCL12 Olaptesed and against the iron metabolism regulatory protein hepcidin -looking Lexaptepid . Use as diagnostics is also possible.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Father A, Klussmann S: Turning mirror-image oligonucleotides into drugs: the evolution of Spiegelmer therapeutics . In: Drug Discovery Today . 20, No. 1, January 2015, pp. 147–155. doi : 10.1016 / j.drudis.2014.09.004 . PMID 25236655 .
- ↑ a b Wlotzka B, Leva S, Eschgfäller B, et al. : In vivo properties of an anti-GnRH Spiegelmer: an example of an oligonucleotide-based therapeutic substance class . In: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA . 99, No. 13, June 2002, pp. 8898-902. doi : 10.1073 / pnas.132067399 . PMID 12070349 . PMC 124395 (free full text).
- ↑ a b Klussmann S, Nolte A, Bald R, Erdmann VA, Fürste JP: Mirror-image RNA that binds D-adenosine . In: Nat. Biotechnol. . 14, No. 9, September 1996, pp. 1112-5. doi : 10.1038 / nbt0996-1112 . PMID 9631061 .
literature
- Father A, Klussmann S: Toward third-generation aptamers: Spiegelmers and their therapeutic prospects . In: Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel . 6, No. 2, March 2003, pp. 253-61. PMID 12669461 .