Strontium bromate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 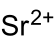
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Strontium bromate | ||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | Sr (BrO 3 ) 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless to slightly yellow, hygroscopic crystals |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
3.773 g cm −3 (monohydrate) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
240 ° C (decomposition) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
373 g l −1 (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Strontium bromate is the strontium salt of bromic acid .
Manufacturing
Strontium bromate can be made by dissolving strontium carbonate in bromic acid.
properties
Strontium bromate is readily soluble in water: 1000 g of saturated solution contains 183.2 g at 0 ° C, 272.5 g at 25 ° C and 410 g at 104 ° C. It usually occurs as the monohydrate Sr (BrO 3 ) 2 · H 2 O, which is converted into the anhydrate at 75.5 ° C with the release of water of crystallization .
The monohydrate crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system in the space group I 2 / c (space group no. 15, position 6) with the lattice parameters a = 8.8742 Å , b = 7.609 Å, c = 9.3748 Å and β = 91.27 °. The crystals are isomorphic to barium bromate .
When heated, strontium bromate decomposes at 240 ° C into strontium bromide and oxygen .
Like all bromates , strontium bromate can be used as an oxidizing agent.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Dale L. Perry, Sidney L. Phillips: Handbook of Inorganic Compounds . CRC Press, 1995, ISBN 978-0-8493-8671-8 , p. 387 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ R. Abegg , F. Auerbach : Handbuch der inorganic Chemie. Verlag S. Hirzel, Vol. 2, 1908. P. 223 ( full text ).
- ^ William F. Linke: The Solubility of the Strontium Halates. In: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1953 , 75 (23), p. 5797-5800. doi: 10.1021 / ja01119a009 .
- ↑ DL Sastry, MV Rajasekharan, KVS Rama Rao: An X-ray study of strontium bromate monohydrate. In: Zeitschrift für Kristallographie 1980 , 152 (3-4), pp. 333-334. doi: 10.1524 / zkri.1980.152.3-4.333
- ^ LK Templeton, DH Templeton: Structure of barium bromate monohydrate. In: Acta Cryst. 1989 , C45 , pp. 672-673. doi: 10.1107 / S0108270188013071 .
- ^ Richard C. Ropp: Encyclopedia of the Alkaline Earth Compounds . Newnes, 2012, ISBN 0-444-59553-8 , pp. 94 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ C. Rammelsberg : About bromic acid and its salts. In: Pogg. Ann. 1841 , 52 , pp. 79-97 ( full text ).


