Tecnazen
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tecnazen | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 HCl 4 NO 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
odorless, colorless to beige solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 260.89 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.744 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
99 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
304 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Tecnazen is an active ingredient for crop protection and a chemical compound from the group of chlorinated and nitrated benzene derivatives .
Extraction and presentation
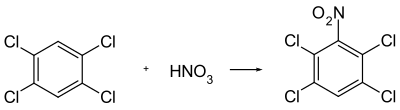
Can tecnazene by nitration of 1,2,4,5-tetra chlorobenzene are obtained.
properties
Tecnazen is an odorless, colorless to beige solid that is practically insoluble in water. It is very stable and only decomposes slowly under UV light .
use
Tecnazen has been used as a fungicide and plant growth regulator. Of the three isomeric tetrachloronitrobenzenes, tecnazene (1,2,4,5-tetrachloro-3-nitrobenzene) has the strongest fungicidal effect.
Admission
Tecnazen was approved as a plant protection product in Germany between 1971 and 1978 .
The EU Commission decided in 2000 not to approve Tecnazen as an active ingredient in the European Union. In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, no pesticides with this active ingredient are permitted.
Web links
- EU: Review report for the active substance tecnazene (PDF; 13 kB), April 12, 2000
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on Tecnazen in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ^ A b c Stanley A. Greene: Sittig's Handbook of Pesticides and Agricultural Chemicals . William Andrew, 2007, ISBN 0-8155-1903-6 , pp. 829 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b Health and Safety Guide (HSG) for Tecnazene , accessed on December 1, 2014.
- ↑ Entry on Tecnazene in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ^ Entry on Tecnazen in the Hazardous Substances Data Bank , accessed on August 13, 2012.
- ↑ György Matolcsy, Miklós Nádasy, Viktor Andriska: Pesticide Chemistry . Elsevier, 1988, ISBN 0-444-98903-X , pp. 806 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Peter Brandt: Reports on Plant Protection Products 2009: Active Ingredients in Plant Protection Products ; Approval history and regulations of the Plant Protection Application Ordinance . Springer, 2010, ISBN 978-3-0348-0028-0 , pp. 26 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Decision of the Commission of November 20, 2000 on the non-inclusion of Tecnazen in Annex I of Directive 91/414 / EEC and the revocation of the approvals for plant protection products with this active substance (PDF) .
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Tecnazene in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; Retrieved February 25, 2016.