Terbinafine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
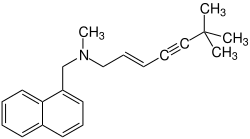
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Terbinafine | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 21 H 25 N | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 291.43 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
195–198 ° C (terbinafine hydrochloride) |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Terbinafine is a drug that is used as an antifungal drug . This is an allylamine - derivative .
application
The active ingredient can be used topically or systemically and is mainly used externally to treat athlete's foot and internally to treat nail fungus (onychomycosis) and is a standard therapeutic agent for severe onychomycoses and dermatomycoses .
effect
Terbinafine inhibit ergosterol - synthesis in the fungal cell membrane. By inhibiting squalene epoxidase, terbinafine blocks the conversion of ( S ) -squalene-2,3-epoxide into lanosterol , the precursor of ergosterol. This results in an accumulation of squalene and an ergosterol deficiency in the cell membrane. In contrast to itraconazole , which blocks the conversion of lanosterol into ergosterol, terbinafine acts earlier in the synthesis path. Ultimately, however, both preparations block the formation of the cell membrane of fungi, for which ergosterol is an essential component.
Trade names
Amiada (D), Amisan (A), Amykal (A), Dermatin (D), Fungizid-ratiopharm extra (D), Helvepidin (CH), Lamisil (D, A, CH), Mayfung (A), Myconormin (D , A, CH), Octosan (D), Pedibene (A), Tineafin (CH), Lamicosil (E), numerous generics (D, A, CH)
literature
- M. Haugh, S. Helou, JP Boissel, BJ Cribier: Terbinafine in fungal infections of the nails: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. In: Br J Dermatol . 147, 2002, pp. 118-121.
- B. Sigurgeirsson, S. Billstein, T. Rantanen, T. Ruzicka, E. di Fonzo, BJ Vermeer, MJ Goodfield, EG Evans: LION. Study: efficacy and tolerability of continuous terbinafine (Lamisil) compared to intermittent itraconazole in the treatment of toenail onychomycosis. Lamisil vs. Itraconazole in Onychomycosis. In: Br J Dermatol. 141 Suppl, 56, 1999, pp. 5-14.
- MH. Schmid-Wendtner: Terbinafine: systemic and topical therapy of fungal infections. ABW-Verlag, Berlin 2006, ISBN 3-936072-44-2 .
Web links
- Entry on terbinafine in Pharmawiki
- Terbinafine ZTC
- Terbinafine tolerance (reading sample)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on terbinafine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 1, 2014.
- ↑ a b Data sheet Terbinafine hydrochloride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 23, 2016 ( PDF ).