Trichophyton mentagrophytes
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
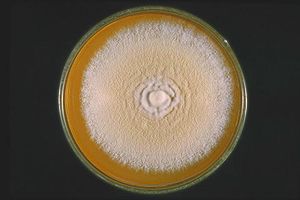
Culture of Trichophyton mentagrophytes |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | ||||||||||||
| ( CP Robin ) Sabouraud , 1895 |
Trichophyton mentagrophytes (sensu stricto) ( syn .: T. mentagrophytes var. Quinckeanum , T. langonii , T. quinckeanum and T. sarkisovii ) is askin fungus ( dermatophyte )thatcolonizesthe horny substance . It occurs mainly in rodents and camels and is therefore to be regarded as a zoophilic dermatophyte. Like all zoophilic dermatophytes, it can alsotrigger dermatophytoses in humans, especially in the head ( tinea capitis ) and body ( tinea corporis ), particularly often in the form of a favus . Like all dermatophytes feeds T. mentagrophytes of keratins . The transmission from animal to animal or animal to person occurs through direct or indirect contact. The teleomorph , i.e. the sexual stage of T. mentagrophytes , belongs to the Arthoderma simii complex .
morphology
Cultures are white, gypsum-like and flat on the surface and have a slightly brownish back. The microconidia are arranged in the shape of spikes and grapes, the macroconidia are short and cigar-shaped with three to five chambers. Microscopically, the fungus cannot be distinguished from Trichophyton interdigitale . Sometimes branched hyphae appear in the shape of a candle holder, which can also lead to confusion with Trichophyton schoenleinii .
Systematics
Older studies distinguished the anthropophilic subspecies T. mentagrophytes var.interdigitale , T. mentagrophytes var.nodulare (synonym T. krajdenii) and T. mentagrophytes var.goetzii as well as the zoophilic subspecies T. mentagrophytes var.granulosum (main host rodents), T. mentagrophytes var. erinacei (main host hedgehogs) and T. mentagrophytes var. quinckeanum (main host mice). Molecular biological studies showed, however, that only T. mentagrophytes var. Quinckeanum can be assigned to the species T. mentagrophytes in the narrower sense ( sensu stricto ). All other subspecies are now included in the T. interdigitale species. In the first description by Charles-Philippe Robin in 1853, the fungus was classified in the genus Microsporum ( M. mentagrophytes ).
literature
- Birgid Neumeister, Heinrich K. Geiss, Rüdiger Braun, Peter Kimmig: Microbiological diagnostics: bacteriology - mycology - virology - parasitology . Georg Thieme, 2nd edition 2009, ISBN 9783131579423 , p. 716.
Individual evidence
- ↑ P. Nenoff, J. Herrmann, Y. Gräser: Trichophyton mentagrophytes sive interdigitale? A dermatophyte in the course of time. In: Journal of the German Dermatological Society . Volume 5, Number 3, 2007, ISSN 1610-0387 , pp. 198-202, doi : 10.1111 / j.1610-0387.2007.06180.x . PMID 17338794 . (Review).