Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase
| Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 406 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Homotetramer | |
| Cofactor | Hamm | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | TDO2 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 1.13.11.11 , dioxygenase | |
| Response type | Oxidation with the incorporation of two oxygen atoms | |
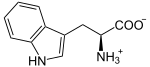
| Substrate | L-tryptophan + O 2 | |
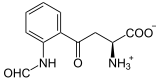
| Products | N-formylkynurenine | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase | |
| Parent taxon | Creature | |
Tryptophan-2,3-Dioxygenase (TDO) is an enzyme that oxidizes L- Tryptophan by binding to two oxygen atoms . This is the first and at the same time rate-determining reaction step in the breakdown of tryptophan. TDO occurs in most living things. In humans, it is mainly produced in the liver . An active TDO enzyme consists of a tetramer and binds two molecules of heme as a cofactor in the catalytic center.
TDO supplements itself in the body with indolamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), which catalyzes the same breakdown; However, the IDO uses superoxide anions instead of oxygen and is localized in the immune system and the placenta .
Catalyzed reaction
L -ryptophan is oxidized to N -formyl- L -kynurenine . The hamming molecule stabilizes the substrate (tryptophan). As with all dioxygenases , the iron atom of the heme is involved in the oxidation of tryptophan. Other tryptamines such as serotonin are also accepted as a substrate .
regulation
The transcription of TDO is influenced by the presence of glucocorticoids and heme . The enzyme activity of TDO is modulated by insulin and can be inhibited by the drugs acyclovir , tolmetin and sulindac .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b UniProt P48775
- ↑ BioGPS entry
- ↑ Liao M, Pabarcus MK, Wang Y, et al : Impaired dexamethasone-mediated induction of tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase in heme-deficient rat hepatocytes: translational control by a hepatic eIF2alpha kinase, the heme-regulated inhibitor . In: J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. . 323, No. 3, December 2007, pp. 979-89. doi : 10.1124 / jpet.107.124602 . PMID 17761498 .
- ↑ Isenović ER, Zakula Z, Koricanac G, Ribarac-Stepić N: Comparative analysis of tryptophan oxygenase activity and glucocorticoid receptor under the influence of insulin . In: Physiol Res . 57, No. 1, 2008, pp. 101-7. PMID 17223727 .
- ↑ Müller AC, Daya S: Acyclovir inhibits rat liver tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase and induces a concomitant rise in brain serotonin and 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid levels . In: Metab Brain Dis . 23, No. 3, September 2008, pp. 351-60. doi : 10.1007 / s11011-008-9095-4 . PMID 18665439 .
- ↑ Dairam A, Antunes EM, Saravanan KS, Daya S: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, tolmetin and sulindac, inhibit liver tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase activity and alter brain neurotransmitter levels . In: Life Sci. . 79, No. 24, November 2006, pp. 2269-74. doi : 10.1016 / j.lfs.2006.07.028 . PMID 16952380 .