vicinal
In chemistry , vicinal (usually abbreviated as vic , from the Latin vicinus "neighbor") means that two functional groups (e.g. halogens such as fluorine , chlorine or bromine ) are bound to two neighboring carbon atoms . The use of the term vicinal is usually restricted to two identical functional groups.
| Comparison of vicinal with geminal and isolated substitution patterns | ||||
| Alkane | geminal | vicinal | isolated | |
| methane |

|
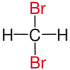
|
does not exist | does not exist |
| Ethane |
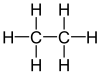
|
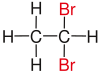
|
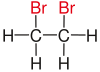
|
does not exist |
| propane |
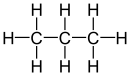
|
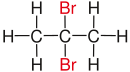
|

|
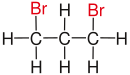
|
| Red marked substituents on selected dibromoalkanes. | ||||
The term vicinal is also used to describe trisubstituted benzene and heterocycles. 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene is z. B. designated as vic -trimethylbenzene.
Further terms describing the relative arrangement of two functional groups are geminal and α and β positions .
1 H-NMR spectroscopy
In 1 H- NMR spectroscopy , the coupling of two hydrogen atoms located on adjacent carbon atoms is referred to as vicinal coupling . The vicinal coupling constant is referred to as 3 J because the hydrogen atoms couple with each other through three bonds. Depending on the other substituents, the vicinal coupling constant assumes values between 0 and +20 Hz. The dependence of the vicinal coupling constant on the dihedral angle is described by the Karplus relationship .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Otto-Albrecht Neumüller (Ed.): Römpps Chemie-Lexikon. Volume 6: T-Z. 8th revised and expanded edition. Franckh'sche Verlagshandlung, Stuttgart 1988, ISBN 3-440-04516-1 , p. 4511.
- ^ Brockhaus ABC Chemie , VEB F. A. Brockhaus Verlag, Leipzig 1965, p. 1502.
- ^ DH Williams, I. Fleming: Structure clarification in organic chemistry; An introduction to spectroscopic methods , 6th revised edition, Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 1991, p. 105.

