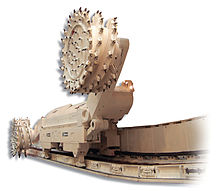
Shearer loader

In hard coal mining, a shearer loader, or shearer loader for short , is a mining machine in a face . Shearer loaders are used in mining in cutting extraction .
history
A British patent for a roller shearer was granted as early as 1912. Another patent followed in 1929. However, these patents were not put into practice because they did not provide an improvement over a shearer loader. The first coal extraction and loading machine was built in 1925 by the Knapp machine factory in Wanne-Eickel. A short time later this machine was equipped with a cutting frame by the Knapp company. However, due to its technical imperfections, this machine did not bring the desired success and the miners lost their interest in it. In 1934 the first cutter loader was used in Great Britain. In the German mining industry, the so-called Iron Miner was used at the Rheinpreußen colliery in 1938 . Almost at the same time as the Iron Miner, several mining and loading machines were developed. These machines were based on a cutting chain and detaching units that detached the undercut coal from the bond . They also drew a loading device that loaded the coal into the faceplate . In 1942 the prototype of a cutter loader from the Eickhoff company was tested at the Jacobi colliery. This machine was a combination of a chain cutting machine with a height-adjustable bar cutting machine and a cross conveyor. The machine pulled itself along the coal face with an integrated winch. The joint was undercut by the cutting arm running ahead. The material gained from the cutting bar in the hanging wall slid over a protruding baffle plate into the cross conveyor. It is not known whether this machine, known as the " Iron Heinrich ", got beyond its prototype status; it is uncertain whether it will be used in any other way than the one at the Jacobi mine . From the beginning of the 1950s, new developments of shearer loaders came onto the market. Shearer loaders became widespread from the beginning of the 1970s as extraction machines for fully mechanical cutting extraction in mining.
developments
The first conventional shearer loader was equipped with a rigid shearer. To move the machine, it was equipped with a cable winch and later a chain winch. It was equipped with additional cutting devices for use in thick seams. These cutting devices were used to cut up the coal undercut by the rigid roller and to extract it. An attached box scraper functioned as an additional cutting device; in later models it was replaced by an attached portal scraper. With these types of machines, the one-sided mode of operation was disadvantageous, which made it necessary to take a clearing drive in addition to the mining drive. This lost recovery time. In addition, in the case of individual ram dismantling, the dismantling could only be brought in after the clearance drive, which in turn had a negative effect on the hanging wall. As the next modification, a planing system was attached to the shearer loader with a rigid roller . It served as a second extraction facility, whereby the coal could be removed in both directions of travel of the shearer loader. In one roll cut, the top coal was extracted up to the hanging wall with the cutter roller and the bottom coal up to the horizontal with the planer. The clearing drive could be omitted and the longwall construction could be brought in promptly. Further changes were shearer loaders with two internal pivoting rollers, later with external pivoting rollers.
construction
A shearer loader consists of a machine slide with a built-in electric drive , the cutting motor for the cutting rollers and the drive. The cutting winch is operated hydraulically and driven by means of cutting chains via a chain wheel. The shearer loader can also be moved back and forth without the shearer turning. In modern shearer loaders, the shear rollers are located at the ends of the support arms, which are movably flanged to both ends of the gearbox housing . The roller support arms contain a gear wheel cascade for power transmission to a planetary gear. The cutter roller is driven by the planetary gear. The height of the roller support arm is adjusted using hydraulic cylinders . But there are also shearer loaders in which the drive motors for the shearer roller are integrated into the roller support arm. The motors used are water-cooled three-phase motors with an output of up to 230 kilowatts. The propulsion of the machine is also its own electric motor, which via a gear to the armored face conveyor located rack and pinion gearing acts. DC shunt motors are used here. The motors are also water-cooled and have an output of up to 25 kilowatts. The speed of the machine is up to 650 meters per hour, depending on the type. The weight of a shearer loader is up to 50 tons. The electrical supply takes place via a trailing cable , this is led together with the water supply hose in a cable drag chain on the side of the conveyor. All controls and hydraulics are located in the housing of the shearer loader, which is closed on all sides.
business
In operation, the machine moves back and forth in the face, which is up to 450 meters long. The cutting roller located at the front end of the machine cuts a strip of coal out of the hanging wall of the seam , while the lagging roller wins the lying down . Up to one meter of coal seam can be mined per operation. The vertical movement is driven by electrically driven toothed wheels that mesh with a rack (pinion rack) mounted on the chain conveyor. The resulting coal dust is precipitated by water, which is sprayed through nozzles on the roller arms and the cutting rollers. The extracted coal falls onto the chain conveyor, which then transports the coal to the conveyor belt in the footpath. The installed electrical power of a shearer loader can be up to 500 kilowatts , because of the long distance to work, the machine is normally operated via a remote control . In contrast to the coal plow , the shearer loader is mostly used in seams of greater thickness (from approx. 1.8 m). The leading manufacturers of shearer loaders are Gebr. Eickhoff Maschinenfabrik und Eisengießerei in Bochum and Caterpillar (after the takeover of Bucyrus International ), in which Deutsche Bergbau Technik (DBT) (formerly Eisenhütte Westfalia trade union ) in Lünen was merged.
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Walter Bischoff , Heinz Bramann, Westfälische Berggewerkschaftskasse Bochum: The small mining dictionary. 7th edition, Verlag Glückauf GmbH, Essen, 1988, ISBN 3-7739-0501-7 .
- ^ A b Wirtschaftsvereinigung Bergbau eV: The mining manual. 5th edition, Verlag Glückauf GmbH, Essen, 1994, ISBN 3-7739-0567-X .
- ^ A b c d e Heinz Kundel: coal production. 6th edition, Verlag Glückauf GmbH, Essen, 1983, ISBN 3-7739-0389-8 .
- ^ Fritz Pamp: The Jacobi colliery; Their development up to the end of the Second World War. In: Osterfelder Bürgerring. (Ed.): Der Kickenberg, Osterfelder Heimatblatt. No. 24, Walter Perspektiven GmbH, Oberhausen September 2012, ISSN 1864-7294 , pp. 4-6.
- ↑ Ernst-Ulrich Reuther: Introduction to mining. 1st edition, Verlag Glückauf GmbH, Essen, 1982, ISBN 3-7739-0390-1 .
- ^ Carl Hellmut Fritzsche: Textbook of mining science. First volume, 10th edition, Springer Verlag, Berlin / Göttingen / Heidelberg 1961
- ↑ Shearer loader. Patent No. DE4410133A1 September 28, 1995 (accessed September 13, 2011).
- ↑ cnbc.com , CNBC : Caterpillar to Buy Bucyrus in $ 8.6 Billion Deal , November 15, 2010.
Web links
- Picture of a shearer loader in action, here the lagging roller (last accessed on December 14, 2012)
- Animation of a shearer loader in the face (last accessed on December 14, 2012)
- Shearer loader in action. (Video) (accessed September 13, 2011)