2,2-diethoxytetrahydrofuran
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2,2-diethoxytetrahydrofuran | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Diethoxyoxolane |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 16 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 160.21 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4181 ( nD , 25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
2,2-Diethoxytetrahydrofuran is a cyclic orthoester that can be reacted with diols to form biodegradable polyorthoesters .
presentation
The synthesis of 2,2-diethoxytetrahydrofuran by reacting γ- butyrolactone and the Meerwein salt triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate in diethyl ether was first described by Hans Meerwein and co-workers. The electrophilic ethyl cation always superposed in this case to the carbonyl oxygen, forming the isolatable, but extremely hygroscopic solid (mp. 42 ° C) O -ethyl-γ-butyrolactonium tetrafluoroborate, located in dichloromethane , chloroform and 1,2-dichloroethane solves , is insoluble in diethyl ether, benzene and carbon tetrachloride . The onium salt practically quantitatively adds an ethanolate anion from sodium ethanolate in ethanol to the 2,2-diethoxytetrahydrofuran.
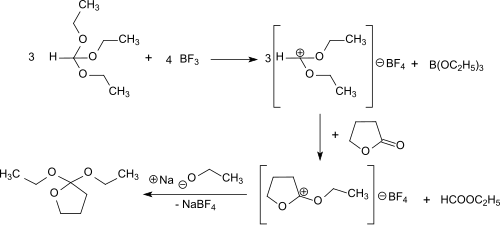
While avoiding the use of diethyl ether as a solvent and its formation as a by-product in the synthesis, as well as the isolation of difficult to handle intermediate products, 2,2-diethoxytetrahydrofuran can also be produced in a one-pot reaction without a solvent with the reactants γ-butyrolactone, triethyl orthoformate and gaseous boron trifluoride . First, diethoxymethylium tetrafluoroborate is formed from the triethyl orthoformate and boron trifluoride at −30 ° C, which attacks the carbonyl group of γ-butyrolactone and converts it to O-ethyl-γ-butyrolactonium tetrafluoroborate. Added sodium ethoxide in ethanol reacts to form the end product, which is obtained in 69% overall yield after distillation .
The reaction proceeds under mild conditions (<0 ° C), and the practically quantitative addition of ethanolate to O- ethyl-γ-butyrolactonium tetrafluoroborate can also be catalyzed by bases such as ammonia and triethylamine .
properties
2,2-Diethoxytetrahydrofuran is a water-clear liquid which, according to the information in the original literature, boils at 60–61.5 ° C under 10 mm Hg vacuum .
use
The cyclic orthoester 2,2-diethoxytetrahydrofuran is a reactive bifunctional monomer that forms biodegradable polyorthoesters of the POE-I type through transesterification with α, ω-diols.
Polyorthoesters are used as embedding media for pharmaceuticals in depot pharmaceutical forms for the controlled release of active ingredients by surface erosion under physiological conditions.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Patent US4990631 : Process for the preparation of 2,2-Dialkoxy cyclic ortho esters derived from lactones. Published February 5, 1991 , Applicant: Alza Corp., Inventor: K. Alster.
- ↑ a b c H. Meerwein, P. Borner, O. Fuchs, HJ Sasse, H. Schrodt, J. Spille: Reactions with alkyl cations . In: Chem. Ber. tape 89 , no. 9 , 1956, pp. 2060-2079 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.19560890907 .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Patent US4990631 : Reacting trialkyl orthoformate with boron trifluoride and lactone, then with alkoxide or alkanol and base. Published February 5, 1991 , Applicant: Alza Corp., Inventor: K. Alster.
- ↑ Jorge Heller: 6. Poly (Ortho Esters) . In: AJ Domb, J. Kost, DM Wiseman (eds.): Handbook of Biodegradable Polymers . Harwood Academic Press, 1997, ISBN 90-5702-153-6 , pp. 99-118 .