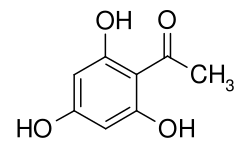
2,4,6-trihydroxyacetophenone
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2,4,6-trihydroxyacetophenone | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 8 O 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
light yellow solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 168.15 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.25 g cm −3 (monohydrate) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
219-221 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
2,4,6-Trihydroxyacetophenone is an aromatic compound which is derived from both acetophenone and phloroglucinol (1,3,5-trihydroxybenzene). The structure consists of a benzene ring with an attached acetyl group (-COCH 3 ) and three hydroxyl groups (-OH) as substituents .
Occurrence
2,4,6-Trihydroxyacetophenone occurs naturally in plants (such as plums and myrtle plants ).
Extraction and presentation
2,4,6-Trihydroxyacetophenone can be obtained by reacting acetic anhydride , acetyl chloride or acetonitrile with phloroglucinol. It is also possible to produce it by reacting acetic acid with phloroglucinol and zinc chloride ( Nencki reaction ).
properties
2,4,6-Trihydroxyacetophenone is a light yellow solid that is sparingly soluble in water. It is an efficient inhibitor of glucose transport in human erythrocytes .
use
2,4,6-Trihydroxyacetophenone is used as a matrix for matrix-assisted laser desorptions / ionizations .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet 2 ′, 4 ′, 6′-Trihydroxyacetophenone monohydrate, 98% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on September 22, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ^ Carl L. Yaws: Thermophysical Properties of Chemicals and Hydrocarbons . William Andrew, 2008, ISBN 978-0-8155-1990-4 , pp. 238 ( books.google.de ).
- ^ A b c William M. Haynes: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 95th Edition . tape 3 . CRC Press, 2014, ISBN 978-1-4822-0868-9 , pp. 530 ( books.google.de ).
- ↑ Eduardo Antonio Ferreira, Eliana Fortes Gris, Jussara Matos Rebello, João Francisco Gomes Correia, Luis Flávio Souza de Oliveira, Danilo Wilhelm Filho, Rozangela Curi Pedrosa: The 2 ′, 4 ′, 6′-Trihydroxyacetophenone Isolated from Myrcia multiflora Has Antiobesity and Mixed Hypolipidemic Effects with the Reduction of Lipid Intestinal Absorption , Planta Med , 2011; 77 (14): 1569-1574, doi : 10.1055 / s-0030-1270956 , PMID 21472649 .
- ↑ Shmuel Yannai: Dictionary of Food Compounds with CD-ROM, Second Edition . CRC Press, 2012, ISBN 978-1-4200-8352-1 , pp. 1917 ( books.google.de ).
- ^ Robert Martin: Handbook of Hydroxyacetophenones . Springer Science & Business Media, 2013, ISBN 978-94-017-1745-8 , pp. 57 ( books.google.de ).
- ↑ 2,4,6-Trihydroxyacetophenon - Lexicon of Biology . ( Spektrum.de ).
- ↑ Data sheet 2 ′, 4 ′, 6′-Trihydroxyacetophenone from AlfaAesar, accessed on September 22, 2017 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
