Acetophenone
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Acetophenone | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 8 O | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless to slightly yellowish, oily liquid with a sweet odor |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 120.15 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
Liquid above 20 ° C, solid below |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.03 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
20 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
202 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.5372 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Acetophenon [ at͡setofeˈnoːn ] (name composed of: Acet yl-, o , phen from the phenyl group and on to denote as ketone) is an aromatic organic - chemical compound and belongs to the ketones . Acetophenone is used, among other things, as a hypnotic and is known as such under the common name Hypnon .
Occurrence
Acetophenone is also a component of many essential oils such as Labdanum , Castoreum and Stirlingia latifolia . This ketone is also found in many natural flavors and in coal tar .
Extraction and presentation
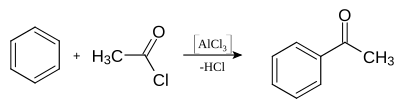
Acetophenone can be produced by Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene with acetic acid chloride or acetic anhydride . In contrast to Friedel-Crafts alkylation , the Lewis acid aluminum chloride (AlCl 3 ) does not act as a catalyst , but is consumed as a reagent in equivalent amounts, with aluminum hydroxide being formed after the necessary hydrolysis of the intermediate product .
properties
Physical Properties
Acetophenone is a colorless to yellowish liquid with a sweet smell reminiscent of orange blossom. The compound boils at 202 ° C. under normal pressure. According to Antoine, the vapor pressure function results from log 10 (P) = A− (B / (T + C)) (P in bar, T in K) with A = 4.64896, B = 2006.397 and C = −43.472 in the temperature range from 310 to 475 K. Acetophenone forms an azeotropic mixture with water at 98 ° C and 82% water.
| property | Type | Value [unit] | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard enthalpy of formation | Δ f H 0 liquid Δ f H 0 gas |
−142.5 kJ mol −1 −86.7 kJ mol −1 |
|
| Standard entropy | S 0 gas | 372.88 J mol −1 K −1 | than gas |
| Enthalpy of combustion | Δ c H 0 liquid | −4148.9 kJ mol −1 | |
| Heat capacity | c p | 227.6 J mol −1 K −1 (25 ° C) | as a liquid |
| Critical temperature | T c | 709.6 K | |
| Critical pressure | p c | 40.1 bar | |
| Critical density | ρ c | 2.59 mol·l −1 | |
| Enthalpy of fusion | Δ f H | 16.65 kJ mol −1 | at the melting point |
| Enthalpy of evaporation | Δ V H | 43.63 kJ mol −1 | at normal pressure boiling point |
Safety-related parameters
Acetophenone forms flammable vapor-air mixtures at higher temperatures. The compound has a flash point of 77 ° C. The lower explosion limit is 1.1 vol.% (55 g / m 3 ), the lower explosion point at 70 ° C. The ignition temperature is 535 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T1. The electrical conductivity is rather low at 3.1 · 10 −7 S · m −1 .
use
Due to its reactive structure, acetophenone is the starting material of numerous syntheses as a starting or intermediate product for other fragrances and pharmaceuticals as well as synthetic resins. It can also be used as a high-boiling solvent for paints and resins.
safety instructions
Acetophenone as a pure substance is harmful if swallowed. It is irritating to the eyes and can cause dermatitis if exposed to unprotected skin . Suitable gloves should be worn as splash protection. In higher concentrations it has a hypnotic effect, hence the synonym hypnon. At a concentration of 80 ppm, the vapors produce severe symptoms of poisoning after exposure for over an hour . Acetophenone is difficult to ignite and not very volatile. The vapors are much heavier than air. Strongly exothermic reactions can occur with strong oxidizing agents and strong bases. Above 300 ° C, acetophenone decomposes. Here can benzene , biphenyl , 1,4-diphenylbenzene , carbon monoxide , methane , hydrogen , ethene and / or toluene arise.
Derivatives
Starting from acetophenone, there are some derivatives with additional hydroxyl and methoxy groups as substituents:
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on ACETOPHENONE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on May 4, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on acetophenone. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on March 3, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Entry on acetophenone in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 28, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-6.
- ↑ Entry on Acetophenone in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Stull, DR: Vapor Pressure of Pure Substances Organic Compounds in Ind. Eng. Chem. 39 (1947) 517-540, doi : 10.1021 / ie50448a022 .
- ^ IM Smallwood: Handbook of organic solvent properties , Arnold London 1996, ISBN 0-340-64578-4 , pp. 183-185.
- ↑ a b c Colomina, M .; Latorre, C .; Perez-Ossorio, R .: Heats of combustion of five alkyl phenyl ketones in Pure Appl. Chem. 2 (1961) 133-135.
- ^ Stull DR, Jr .: The Chemical Thermodynamics of Organic Compounds , Wiley, New York, 1969.
- ↑ Phillip, NM: Adiabatic and isothermal compressibilities of liquids in Proc. Indian Acad. Sci., 1939, A9, 109-120.
- ↑ a b Teja, AS; Rosenthal, DJ: The critical pressures and temperatures of ten substances using a low residence time flow apparatus in Experimental Results for Phase Equilibria and Pure Component Properties in DIPPR DATA Series No. 1, 1991.
- ↑ Teja, AS; Anselme, MJ: The critical properties of thermally stable and unstable fluids. I. 1985 results in AIChE Symp. Ser., 1990, 86, 279, 115-121.
- ↑ Luginin: Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 9 (1911) 223.
- ^ Steele, WV; Chirico, RD; Knipmeyer, SE; Nguyen, A .: in J. Chem. Eng. Data 41 (1996) 1255-1268, doi : 10.1021 / je9601117 .
- ^ A b c E. Brandes, W. Möller: Safety-related parameters - Volume 1: Flammable liquids and gases , Wirtschaftsverlag NW - Verlag für neue Wissenschaft GmbH, Bremerhaven 2003.
- ↑ Technical rule for hazardous substances TRGS 727, BG RCI leaflet T033 Avoidance of ignition hazards due to electrostatic charges , status August 2016, Jedermann-Verlag Heidelberg, ISBN 978-3-86825-103-6 .