3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
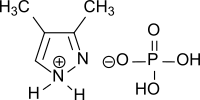
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 11 N 2 O 4 P | |||||||||
| Brief description |
white or light beige, hygroscopic solid |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 194.13 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| Melting point |
167-169 ° C |
|||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water and methanol |
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
3,4-dimethylpyrazole or DMPP is an organic chemical compound , to the heterocycles ( pyrazole - derivatives ) counts. DMPP is a nitrification inhibitor which , even in small amounts when added to fertilizers, inhibits the nitrification of ammonia or ammonium ions (NH 4 + ) to nitrate (NO 3 - ) in the soil.
Manufacturing
To synthesize the 3,4-dimethylpyrazole, 2-butanone (methyl ethyl ketone, MEK) is first reacted with methyl formate (methyl formate) under basic conditions in a Claisen condensation to give the corresponding ketoaldehyde 2-methyl-3-oxobutanal, which is present as sodium enolate . At the same time, the isomeric 3-oxopentanal is also obtained in a side reaction.
Subsequently, under neutral conditions with hydrazine, the 3,4-dimethylpyrazole (DMP) is formed as the main product and 3-ethylpyrazole (3-EP) as a by-product in a ratio of 92: 8 DMP / 3-EP.
For cleaning and better handling as a crystalline substance, the crude DMP is reacted in isopropanol as a solvent with orthophosphoric acid to form the acid addition salt 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate DMPP, which only has a DMP / 3-EP ratio of 99: 1.
The Claisen reaction takes place in 30% sodium methoxide at temperatures below 30 ° C to the enolized ketoaldehyde, which in a strongly exothermic reaction with hydrazine hydrate under controlled temperature and pH control with yields of approx. 75% of the theoretically possible to the 3.4- Dimethylpyrazole reacts as the main product.
Purification of the DMP by forming the phosphate salt in isopropanol gives the best yields (approx. 75% of theory) and leads to an overall yield of approx. 56%.
properties
3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate is a white to slightly brownish, water-attracting, crystalline substance that dissolves in polar solvents such as water or methanol.
Applications
3,4-Dimethylpyrazole phosphate is added as a nitrification inhibitor to liquid, suspended and solid fertilizers on a mineral basis (e.g. calcium ammonium nitrate , calcium ammonium nitrate CAN) and organic (e.g. liquid manure). Nitrification inhibitors such as DMPP (or dicyandiamide ) inhibit the first and rate-limiting step of the nitrification process, the oxidation of ammonium ions (NH 4 + ) to nitrite ions (NO 2 - ) by inhibiting the enzyme ammonium monooxygenase AMO in soil bacteria of the genus Nitrosomonas . This means that more ammonium-N is available for the plants to take up and the disadvantages of plant fertilization , such as nitrate leaching in water and nitrous oxide emissions into the atmosphere, are reduced.
Compared to dicyandiamide, only a tenth of the concentration is required for DMPP.
Admission
DMPP has been approved in Germany since 2001.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Patent WO2011076194 : Process for the purification of pyrazoles. Registered on December 23, 2009 , published on June 30, 2011 , applicant: K + S Aktiengesellschaft, inventor: L. Waldmann, C.-F. Hahn, H. Eckenrath, R. Pasch.
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole Phosphate at Toronto Research Chemicals , accessed on July 30, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Klaus Schwedlick: Organikum, 23rd edition . Wiley-VCH, 2009, ISBN 978-3-527-32292-3 .
- ↑ W. Hofmair: DMPP - a new nitrification inhibitor (active ingredient effectiveness area of application)
- ↑ Johannes Ottow: Microbiology of Soils: Biodiversity, Ecophysiology and Metagenomics . Springer, Berlin a. a. 2011, ISBN 978-3-642-00823-8 , p. 307.


