3-ethylpentane
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 3-ethylpentane | |||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 16 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
highly flammable colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 100.21 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.70 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−118.3 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
93 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
235 mbar (50 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.3934 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
3-Ethylpentane is a chemical compound from the group of aliphatic saturated hydrocarbons . It is one of the nine constitutional isomers of heptane .
Extraction and presentation
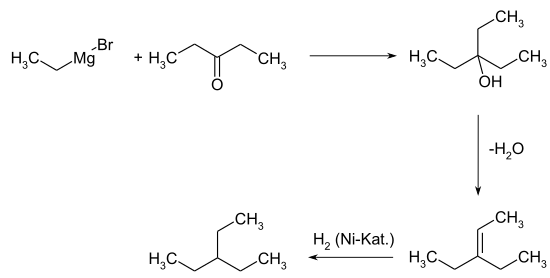
3-ethylpentane occurs in petroleum . The compound can be obtained in small proportions by the isomerization of n-heptane . As early as 1927, a laboratory synthesis was described in which the Grignard compound from ethyl bromide is reacted with 3-pentanone . The resulting 3-ethyl-3-pentanol is used for 3-ethyl-2-pentene dehydrated and then by means of Nickelkatalysor for 3-ethylpentane hydrogenated .
properties
Physical Properties
3-Ethylpentane is a highly flammable and colorless liquid. According to Antoine, the vapor pressure function results from log 10 (P) = A− (B / (T + C)) (P in bar, T in K) with A = 4.00453, B = 1254.119 and C = −53.004 in the temperature range from 294 to 364 K.
The most important thermodynamic properties are listed in the following table:
| property | Type | Value [unit] |
|---|---|---|
| Standard enthalpy of formation | Δ f H 0 gas Δ f H 0 liquid |
−191.4 kJ mol −1 −226.7 kJ mol −1 |
| Enthalpy of combustion | Δ c H 0 liquid | −4814 kJ mol −1 |
| Heat capacity | c p | 219.58 J mol −1 K −1 (25 ° C) as a liquid |
| Enthalpy of fusion | Δ f H 0 | 9.548 kJ mol −1 at the melting point |
| Entropy of fusion | Δ f S 0 | 61.77 kJ mol −1 at the melting point |
| Enthalpy of evaporation | Δ V H 0 | 31.12 kJ mol −1 at the normal pressure boiling point 35.32 kJ mol −1 at 25 ° C |
| Critical temperature | T C | 267.4 ° C |
| Critical pressure | P C | 28.9 bar |
| Critical volume | V C | 0.416 l mol −1 |
| Critical density | ρ C | 2.41 mol·l −1 |
Safety-related parameters
3-Ethylpentane forms highly flammable vapor-air mixtures. The compound has a flash point of −18 ° C.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on 3-ethylpentane in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Streiff, AJ; Murphy, ET; Sedlak, VA; Willingham, CB; Rossini, FD: Purification, Purity, and Freezing Points of 7 Heptanes, 16 Octanes, 6 Pentene, Cyclopentene, and 7 C9H12 Alkylbenzenes of the API-Standard and API-NBS Series in J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. (US) 37 (1946) 331.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-252.
- ↑ Entry on 3-ethylpentane at TCI Europe, accessed on July 11, 2016.
- ↑ Sachanen TO in The Chemistry of Petroleum Hydrocarbons Volume I (Brooks, BT), New York 1954, p. 9
- ↑ Haensel, V .; Donaldson, GR: Platforming of Pure Hydrocarbons in Ind. Eng. Chem. 43 (1951) 2102-2104, doi : 10.1021 / ie50501a036 .
- ↑ Blomsma, E .; Martens, YES; Jacobs, PA: Reaction Mechanisms of Isomerization and Cracking of Heptane on Pd / H-Beta Zeolite in J. Catal. 155 (1995) 141-147, doi : 10.1006 / jcat.1995.1195 .
- ↑ Edgar, G .; Calingaert, G .; Marker, RE: The preparation and properties of the isomeric heptanes. Part I. Preparation in J. Am. Chem. Soc. 51 (1929) 1483-1491, doi : 10.1021 / ja01380a027 .
- ↑ Forziati, AF; Norris, WR; Rossini, FD: Vapor Pressures and Boiling Points of Sixty API-NBS Hydrocarbons in J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. (US) 43 (1949) 555-567.
- ↑ a b c Davies, GF; Gilbert, EC: Heats of combustion and formation of the nine isomeric heptanes in the liquid state in J. Am. Chem. Soc. 63 (1941) 2730-2732, doi : 10.1021 / ja01855a064 .
- ↑ a b c Huffman, HM; Gross, ME; Scott, DW; McCullough, IP: Low temperature thermodynamic properties of six isomeric heptanes in J. Phys. Chem. 65 (1961) 495-503, doi : 10.1021 / j100821a026 .
- ↑ a b Majer, V .; Svoboda, V .: Enthalpies of Vaporization of Organic Compounds: A Critical Review and Data Compilation , Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, 1985, p. 300.
- ↑ a b c d Daubert, TE: Vapor-Liquid Critical Properties of Elements and Compounds. 5. Branched Alkanes and Cycloalkanes in J. Chem. Eng. Data 41 (1996) 365-372, doi : 10.1021 / je9501548 .