Abemaciclib
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
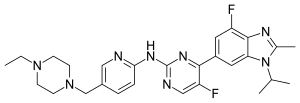
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Abemaciclib | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 27 H 32 F 2 N 8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
CDK inhibitor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
Antineoplastic |
||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 506.61 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Abemaciclib is a medicine used to treat certain types of breast cancer . It is a member of the new class of active ingredients, the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, and is orally effective.
It was approved in the USA on September 28, 2017 as part of the accelerated approval process of the FDA ( Break Through Therapy ), in the European Union one year later on September 27, 2018.
application
Abemaciclib is used with fulvestrant or as monotherapy for the treatment of HR- positive, HER2 -negative, or metastatic breast cancer.
pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Like other CDK inhibitors, Abemaciclib inhibits the cyclin-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK6, which - after activation by binding to cyclin D - are responsible for phosphorylation and thus deactivation of the retinoblastoma protein , a tumor suppressor . This affects the cell cycle during the transition from phase G1 (growth phase) to phase S (synthesis phase) and prevents the breast cancer cells from reaching the S phase, which results in cell senescence and cell death ( apoptosis ). The cell proliferation is thus reduced.
Pharmacokinetics
The absolute bioavailability after oral administration of 200 mg averages 45%. The maximum plasma concentration occurs after an average of 8 hours (4.1 - 24 hours).
Abemaciclib is largely bound to plasma proteins (mean 96.3%) . Excretion occurs primarily in the faeces (on average 81%, mainly metabolites ) and to a lesser extent in the urine (on average 3%). The mean plasma half-life is 18.3 hours.
Side effects
The most common side effects reported were diarrhea , nausea, vomiting, reduction in the number of white blood cells ( leukopenia , neutropenia ) and red blood cells ( anemia ) and platelets ( thrombocytopenia ), stomach pain, infection, fatigue, loss of appetite and headache.
Interactions with other drugs and with food intake
Since abemaciclib is primarily metabolized by the liver enzyme cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) , active substances that inhibit this enzyme (e.g. ketoconazole ) or induce it (such as rifampicin ) have an effect on the plasma concentrations of abemaciclib. If CYP3A4 is inhibited, the concentration increases and vice versa .
One study found no clinically relevant differences between eating and eating without food.
Chemical-physical properties
Abemaciclib is polymorphic , form III is used pharmaceutically. It is a white to yellow non-hygroscopic powder that is practically insoluble in water and sparingly soluble in ethanol. The solubility depends on the pH value .
Early benefit assessment according to § 35a SGB V
In 2018 and 2019, IQWiG examined in two dossier evaluations and two addenda whether active ingredient combinations with abemaciclib in women with HR-positive, HER2-negative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer had an additional benefit compared to the ACT specified by the Federal Joint Committee (G-BA) .
According to IQWiG, there is an indication of lesser benefit for abemaciclib with aromatase inhibitor in initial endocrine therapy after menopause compared to the ACT; For endocrine subsequent therapy and / or women before or in the menopause, an added benefit has not been proven due to a lack of study data. In its decision, the G-BA came to the conclusion “additional benefit not proven” for all four situations (initial or subsequent therapy, before, during or after menopause).
According to the IQWiG, there is a hint of lesser benefit for abemaciclib with fulvestrant in initial or subsequent endocrine therapy for women after menopause compared to the ACT; for women before or during menopause, an added benefit has not been proven due to a lack of suitable study data. According to the G-BA decision, an additional benefit has not been proven for any of the four situations (initial or subsequent therapy, before, during or after the menopause).
Preparation names
- Eli Lilly and Company : Verzenios (EU) Verzenio (USA, J)
literature
- James M. Martin, Lori J. Goldstein: Profile of abemaciclib and its potential in the treatment of breast cancer ; Onco Targets Ther. , 2018, 11, pp. 5253-5259; doi: 10.2147 / OTT.S149245 , PMID 30214230 , PMC 6120573 (free full text).
Web links
Public Assessment Report (EPAR) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for: Abemaciclib
Individual evidence
- ^ Protein Kinase Inhibitors as Sensitizing Agents for Chemotherapy . Academic Press, 2018, ISBN 978-0-12-812738-4 , pp. 140 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b Safety Data Sheet. (PDF) In: achemblock.com. December 2017, accessed on March 17, 2019 .
- ↑ FDA approves new treatment for certain advanced or metastatic breast cancers , PM FDA dated September 28, 2017, accessed December 4, 2017
- ↑ Abemaciclib: Third Cdk4 / 6 inhibitor approved in Europe. In: Cancer Information Service. German Cancer Research Center, October 8, 2018, accessed on March 17, 2019 .
- ↑ Entry on abemaciclib in the DrugBank of the University of Alberta , accessed on March 17, 2019.
- ↑ a b c d HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION (VERZENIO). (PDF) September 2017, accessed on March 17, 2019 (English).
- ↑ Abemaciclib. In: drugs.com. October 8, 2018, accessed March 17, 2019 .
- ↑ Abemaciclib in tablet form is bioequivalent to capsules. In: medonline.at. December 7, 2017, accessed March 17, 2019 .
- ↑ Assessment report Verzenios . European Medicines Agency Committee on Medicinal Products for Human Use , July 2018.
- ↑ A18-72 Abemaciclib in combination with an aromatase inhibitor (breast cancer) - benefit assessment according to Section 35a SGB V , accessed on July 5, 2019.
- ↑ A19-24 Abemaciclib (breast cancer; combination with an aromatase inhibitor) - Addendum to Commission A18-72 , accessed on July 5, 2019.
- ↑ Resolution of the Federal Joint Committee of May 2nd , 2019 on an amendment to the Drugs Directive (AM-RL): Annex XII - Abemaciclib (breast cancer, in combination with an aromatase inhibitor) , accessed on June 24, 2019.
- ↑ A18-73 Abemaciclib in combination with fulvestrant (breast cancer) - benefit assessment according to Section 35a SGB V , accessed on July 5, 2019.
- ↑ A19-25 Abemaciclib (breast cancer; combination with fulvestrant) - Addendum to Commission A18-73 , accessed on July 5, 2019.
- ↑ Resolution of the Federal Joint Committee of May 2nd , 2019 on an amendment to the Drugs Directive (AM-RL): Annex XII - Abemaciclib (breast cancer; in combination with fulvestrant) , accessed on July 5, 2019.