Afoxolans
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
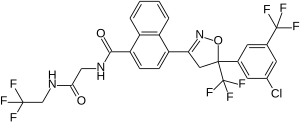
|
||||||||||
| Structural formula without stereochemistry | ||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Afoxolans | |||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 26 H 17 CIF 9 N 3 O 3 | |||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
Inhibition of the chloride channels |
|||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 625.9 g · mol -1 | |||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Afoxolaner is a chemical compound from the isoxazoline group , which is effective as an insecticide and acaricide . It is used to control fleas and ticks in dogs and is effective orally. Afoxolaner can be used for the treatment of acute infestations and for prevention. It is also effective for demodicosis . In a fixed combination with milbemycin oxime , Afoxolaner is used for the simultaneous control of roundworms , hookworms , whipworms and heartworms in dogs.
Mechanism of action
The effect of Afoxolaner is based on the inhibition of ligand-gated chloride channels , in particular the GABA receptor , which leads to selective neuronal overstimulation in parasites . The parasites absorb the active ingredient when they suck their blood and die. Fleas are killed within 2 to 6 hours of contact with the active ingredient, which prevents eggs from being laid. In the case of ticks , the effects mostly occur within 12 hours - at the latest within 24 hours. This reduces the risk of disease transmission, as most pathogens need 16 to 48 hours to get from the tick intestine to the host animal. In a current study, there was no transmission of pathogens from ticks infected with Babesia after a single dose .
Afoxolaner is rapidly absorbed, accumulates in the plasma and is excreted in unchanged form mainly in the bile . With the appropriate dosage, the active ingredient is suitable for puppies as well as adult dogs of all breeds, including those with an MDR1 defect .
Finished medicinal products
- Monopreparation : NexGard
- in fixed combination with milbemycin oxime : NexGard Spectra
literature
- Charlotte Barth: Oral ectoparasite treatment: flexible and needs-based . In: Der Praktische Tierarzt 96, Heft 4 (2015), pp. 402–403.
Web links
- NexGard on the website of the European Medicines Agency
- NexGard Spectra on the European Medicines Agency website
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ F. Beugnet, L. halos, D. Larsen, C. de Vos: Efficacy of oral afoxolaner for the treatment of canine generalized demodicosis. In: Parasite. Volume 23, 2016, p. 14, doi : 10.1051 / parasite / 2016014 , PMID 27012161 , PMC 4807374 (free full text).
- ↑ Frederic Beugnet et al .: Afoxolaner against fleas: immediate efficacy and resultant mortality after short exposure on dogs. In: Parasite2014 / 21 . 2014, p. 42 .
- ↑ Lénaig Halos et al .: Immediate efficacy and persistent speed of kill of a novel oral formulation of afoxolaner (NexGard ™) against induced infestations with Ixodes ricinus ticks. In: Parasites & Vectors . 2014, p. 452 .
- ↑ Frederic Beugnet et al .: The ability of an oral formulation of afoxolaner to block the transmission of Babesia canis by Dermacentor reticulatus ticks in dogs. In: Parasites & Vectors . 2014, p. 283 .