Alamak
|
Double star γ Andromedae / Alamak |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Observation dates equinox : J2000.0 , epoch : J2000.0 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AladinLite | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Constellation | Andromeda | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right ascension | 02 h 03 m 54 s | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| declination | + 42 ° 19 ′ 45 ″ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Apparent brightness | 2.26 mag | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Astrometry | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radial velocity | (−11.7 ± 0.9) km / s | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| parallax | (9.19 ± 0.73) mas | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| distance | (355 ± 28) ly ((109 ± 9) pc ) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Proper movement : | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rec. Share: | approx. +43 mas / a | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dec. portion: | approx. −51 mas / a | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| orbit | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| period | BC: 64 years Bab: 2.67 days |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Individual data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Names | A; BC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Observation data: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Apparent brightness | A. | 2.3 mag | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BC | 4.8 likes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Typing: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectral class | A. | K3 IIb | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BC | Bab: B8 V C: A0 V |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other names and catalog entries |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Alamak or Almaak , named after Bayer γ Andromedae (Gamma Andromedae, short γ And), is a star system in the constellation Andromeda that is about 355 light-years away .
In 1778 Johann Tobias Mayer discovered that Alamak is a double star . It can be resolved with relatively small telescopes, even in the daytime with an eight-inch telescope . The two components with the designations γ 1 Andromedae and γ 2 Andromedae currently have an angular distance of 9 " , 6 and a position angle of 63 °.
The main star γ 1 Andromedae (or γ And A) is a bright red giant of the spectral class K3. Its apparent brightness is 2.26 mag and its surface temperature about 4500 Kelvin. Its diameter is around 80 times larger than that of the sun and its luminosity exceeds that of the sun by around 2000 times.
Γ 2 Andromedae is a triple system with a total brightness of 4.84 mag. First, Wilhelm Struve was able to resolve the two components B and C, which were less than an arc second apart in Pulkowa in October 1842, the former being 5.5 mag and the latter 6.3 mag. Spectrograms made from 1957 to 1959 showed that B is again a spectroscopic binary star with an orbital period of 2.67 days, which consists of two blue and white main sequence stars of the spectral class B9.5. γ Andromedae C is a main sequence star of the spectral class A0. Components B and C revolve around each other in 63.7 years. The orbit has a semi-major axis of 0 ", 30, or 33 Astronomical Units (AU), but because of their eccentricity, the two components can be between 13 AU and 52 AU apart.
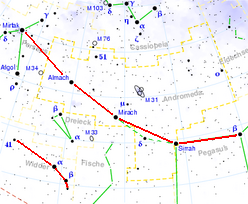
Alternative spellings for Alamak and Almaak are Almach, Almaach and Almak, derived from Arabic عناق الأرض, DMG ʿināq al-arḍ 'Embrace of the ground, desert lynx '. The star is part of the bright five-star sequence (Perseus-Andromeda-Pegasus), which can be seen almost all year round in the northern hemisphere.
The IAU has on 20 July 2016 the proper name Almach as standardized proper name for the star γ 1 defined. The stars of γ 2 therefore have no proper names (yet).
See also
Web links
- SAO entries at VizieR
- CCDM entries at VizieR
Individual evidence
- ↑ SIMBAD Query
- ↑ Almach with Jim Kaler, Stars .
- ↑ Bulletin of the IAU Working Group on Star Names, No. 1, July 2016. (PDF; 184 kB) Retrieved on November 9, 2016 (English).
