Anti-noise
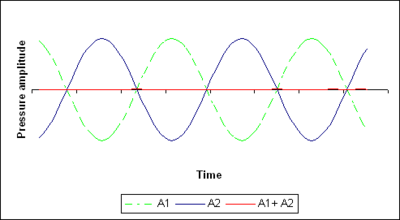
Among anti-sound (also active noise compensation , English Active Noise Reduction [ANR] or Active Noise Cancellation [ANC] ) it is colloquially sound generated artificially in order by means of destructive interference extinguish sound. For this purpose, the aim is to generate a signal that corresponds exactly to that of the disturbing sound with opposite polarity .
Energy conservation
There are two different problems to be distinguished:
- If a noise source emits sound, an attempt is made to use “counter-sound” from another location to reduce the resulting amplitude (and thus the sound energy) in some limited areas through destructive interference . In contrast, the sound energy increases in neighboring areas, as energy is not absorbed at any point , but only redistributed. So far it has not been possible to calm a volume of several wavelengths as a whole . So far, only active sound absorption in pipes has been successful (linear problem).
- In a sufficiently small closed area with dimensions smaller than λ / 4 (as between the ear and headphones), the headphone membrane acts like a movable wall, which ensures approximately constant total pressure ( see also acoustic short circuit ). A distinction is to be made between sound insulation , in which incident sound is converted into thermal energy. This only prevents reflection.
Applications
headphone
In headphones with active noise suppression , a built-in microphone is used to measure the ambient noise and, with the aid of the acoustic transfer function of the headphones, the amount that would remain on the ear is calculated. For this part, an opposite polarity signal is generated in the headphones for compensation. The sound from the outside and the signal from the listener meet as sound at the eardrum . The sound pressure level is significantly reduced. In addition, useful sound (speech, music) can also be reproduced via the headphones.
Even headphones with active noise reduction systems cannot completely eliminate background noise. On the one hand, every person has a different inner and outer ear shape, so that only a precise adjustment in the laboratory would allow complete neutralization. On the other hand, the skull bones also transmit sound to the eardrum (" structure-borne sound "); this proportion cannot be influenced with Active Noise Reduction.
ANR is particularly suitable for attenuating low frequencies where wavelengths are large compared to the dimensions of the headphones. Only here does the sound have a similar phase over the entire surface of the headphones, so that it can be completely attenuated by an anti-phase signal. This method has little effect at high frequencies, since different phase positions then occur on the headphone surface and these also become dependent on the direction of incidence of the sound. In extreme cases, the sound can also be amplified at certain points at high frequencies. Since close-fitting headphones can attenuate high frequencies well, but low frequencies only very poorly, ANR can be used to improve the lack of attenuation of headphones at low frequencies.
The reason for the development of such headphones was the need for noise protection for pilots. ANR headphone / microphone combinations ( headsets ) can be used in aviation - for helicopter pilots, for example - to ensure an environment that is as fatigue-free as possible for the cockpit staff. The rotor noise contains extremely strong low-frequency components that are only slightly attenuated by headphones. Due to the masking effect , higher-frequency signals that are required for voice communication are also concealed, so that the volume of the headphones must be increased very significantly in order to be able to understand air traffic control at all. If the low-frequency rotor noises are attenuated using this method, the communication volume of the headphones can be reduced significantly.
In contrast to simple headphones, ANR headphones require their own power source. A small battery (for example AA or AAA) or a rechargeable battery is sufficient for this, as the ANR electronics only require a small amount of electrical power.
Active noise canceling in consumer headphones
Not only because ANR is established in industry and is already being used in many areas, but also because more and more people are traveling, active noise suppression has meanwhile also become a fixture in consumer products. Often over-ear headphones are used because their design already provides a noticeable reduction in ambient noise. By using active noise canceling, i.e. anti-noise, annoying engine noises or the roar of aircraft turbines can be effectively extinguished.
In the meantime, however, there are also more and more in-ear headphones and true wireless in-ear headphones that use anti-noise. These headphones are much smaller and handier than over-ear headphones and are therefore easier to transport.
PA technology
In public address technology, active noise suppression is used e.g. B. used at large events, as the subwoofers designed for such events cause very strong vibrations with correspondingly low tones. In this application, a loudspeaker is directed in the opposite direction of the other loudspeakers (mostly stage ), which then generates an anti-noise signal under processor control in order to reduce the sound exposure in a certain area.
Active exhaust silencer for motor vehicles
New sound absorbers that work with anti- noise are technically capable of lowering the sound of cars by up to 20 dB (A) compared to classic silencers. A noise reduction of 20 dB (A) is perceived as a reduction of the noise by a quarter.
The electronic counter silencers are smaller and lighter than classic silencers. The reduced back pressure has the effect of either increasing the output or reducing fuel consumption and CO 2 emissions.
Further
The anti- noise principle is used in connection with conventional silencers in ducts and pipelines to attenuate low frequencies in a small installation space. Conventional (passive) silencers require large volumes in order to be effective even at low frequencies. A new area of application has been found in automotive technology, where the passenger compartment of cars can be "calmed down" using Active Noise Cancellation , for example in the Audi A8 or the Honda Legend .
Further applications are being or have been researched, B.
- for the insulation of aircraft engines,
- to reduce the noise level in aircraft ( De Havilland DHC-8 , SAAB 340B +, SAAB 2000, Raytheon Beech King Air 350, Raytheon Beech 1900D, Raytheon Beech King Air 90, 200, 300 and Twin Commander),
- to change the sound of car engines,
- to reduce the low-frequency hum of power transformers in substations ,
- to improve the sound insulation of windows,
- to create zones of calm in open-plan offices,
- to combat high noise levels in printing machines,
- to reduce the noise of wind turbines,
- to reduce noise exposure in magnetic resonance tomographs ,
- for suppressing standing waves in cuboid rooms that occur when playing music or film sound, see Double Bass Array ,
- to reduce noise pollution in motorcycle helmets.
In almost all applications, a similar effect can be achieved in another way at lower costs and without additional energy input. Therefore, the application is usually limited to special applications.
Similar procedures
A similar process is used on the Baltic Cable high-voltage direct current transmission line to suppress high-frequency interference signals that arise during converter operation.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ US Patent 2043416 of 1934
- ↑ a b 3sat media library. Retrieved July 6, 2020 .
- ↑ a b heise online: Video: With noise against noise - How modern technology turns loud cars into whispering street cruisers. Retrieved July 6, 2020 .
- ^ Space travel: First "whisper aircraft" in five years , welt.de December 23, 2008.
- ↑ Ultra Electronics Ultra Quiet Cabin
- ↑ Technology - anti-noise ensures new engine sound Heise.de Automobiles, from October 9, 2009.
- ↑ "Anti-noise" allows wind turbines to generate higher electricity , Pressetext.at August 1, 2008.
- ↑ Anti-noise against tomograph noise