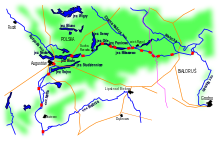
Augustów Canal
The Augustów Canal ( Belarusian Аўгустоўскі канал Awgustow Canal , Polish Kanał Augustowski ) near Augustów is an artificial waterway built in the 19th century that crosses Polish and Belarusian territory.
Meaning and historical background
When Prussia introduced unusually high customs duties for the transit of Polish goods through Prussian territory in 1821, the waterway across the Vistula to the Baltic Sea was practically cut off for Poland. So Poland was forced to look for alternatives. The Polish Minister of Economic Affairs, Franciszek Ksawery Drucki-Lubecki , came up with the idea of opening a new trade route that would bypass Prussian territory in the north of Poland and connect with the port of Ventspils ( Windau ).
The Polish general Ignacy Pradzyński developed the concrete plan to connect the Vistula and Memel by a canal as a first step . In a further section the Memel tributary Dubysa was to be connected to the Venta in order to create a continuously navigable connection to the Russian port of Ventspils. A southern option to the Black Sea was also considered.
The Augustów Canal, named after the city it crossed in north-eastern Poland, with which the connection between the Vistula and Memel was created, was built. The construction work lasted from 1823 to 1839. The canal system began with the Dębowo lock on the Biebrza River, south of Augustów, and ended with a lock to the Memel north of the city of Hrodna, which was then part of the Russian Empire . The waterway, which also included several canalized rivers and led through numerous lakes, reaches a length of 101 kilometers. 18 locks were built to overcome the height difference of 55 meters . A two-chamber lock was built near the Polish town of Paniewo.
The Augustów Canal itself was only part of the originally planned connection to Ventspils - since the lower reaches of the Memel also lay on Prussian territory, this should have been bypassed. Work on the Venta-Dubysa Canal was abandoned. a. also because Prussia had meanwhile shown concession on the customs question.
With the creation of the Polish Corridor by the Versailles Treaty (1919), Poland regained direct access to the Baltic Sea and the Augustów Canal lost its economic importance. After the border was drawn in 1945, 80 kilometers of the canal with 14 locks were on Polish territory. Today it is only used for tourism and recreational shipping. In 2007 the Belarusian side was renovated, since then this waterway has been open again.
General information
Length of the canal: 101 km (of which 82 km in Poland)
Forming the canal (apart from the 18 locks):
- the Netta river
- the Czarna Hańcza river, one of the most important rivers in the Suwalk region (Polish: Suwałki)
- the Augustus Lakes (group of lakes in Podlaskie Voivodeship )
Many water birds inhabit the canal area: swans, ducks and geese. The fish found in the channel include: tench , bream , perch, pike, eel, crucian carp , burbot , roach and bleak .
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Mieczysław, Jackiewicz: Litwa: podróż sentymentalna 2006. (Polish)
- ^ Augustów Canal - Regional Water Management Authority in Warsaw (RZGW Warsawa) . Archived from the original on March 22, 2012. Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved April 27, 2011.
- ^ Russian Commerce in the Black Sea . In: The Bankers' magazine . January 1855, p. 500.
Web links
- Description at UNESCO (English)
- www.suwalszczyzna.pl (English)
- Information on visa-free visits to the Awgustow Canal Park for foreigners. Embassy of the Republic of Belarus in the Federal Republic of Germany, 2013, accessed on June 9, 2019 .
Coordinates: 53 ° 52 ′ 0 ″ N , 22 ° 58 ′ 0 ″ E