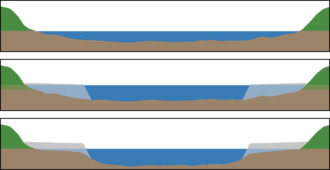
River straightening
When a river is straightened , the naturally occurring meanders of a river are pierced at their necks . This makes the course of the river shorter and straighter; the water flows faster. An oxbow lake can arise from the cut river bend (the meander curve) . River straightening is a measure of river engineering .
history
Although the Romans built a large number of water pipes and aqueducts , they rarely intervened directly in the river landscapes, for example when the Velino River was diverted into the Nera in 271 BC. BC , which resulted in the Cascata delle Marmore, the highest artificial waterfall in the world to this day. It was not until the late Middle Ages that people increasingly began to correct bodies of water, including through river straightening.
Around 1360, the main arm of the Danube was brought up to the city of Ingolstadt (see Sandrach ).
In 1391 the first attempt to straighten the loop of the Rhine near Liedolsheim was documented in Germany .
Goal setting
River straightening is often used to make the river usable for shipping . Sometimes land reclamation or the permanent definition of state , community and property boundaries are also in the foreground. If the course of the river is structurally determined, flood protection can even be achieved with appropriate hydraulic engineering measures, such as planned retention areas. As a rule, however, straightening increases the flood problems.
Malaria was eradicated in Germany in the 1960s by the silting up of oxbow lakes as a result of river straightening . However, the other species diversity also decreased.
In the case of rivers rich in sediment, in addition to piercing the river loops or surrounding mountains , a relatively low bank reinforcement was carried out using fascines , which were below the flood line. During floods, the river bed could expand into the floodplain , which again reduced the flow velocity somewhat. Debris could sediment and increase the land behind the dam.
However, after the hinterland was raised several times, a flood dam was often built and the resulting hinterland built on, which increased the flow speed and the water level extremely sharply in the event of a flood.
Application examples
In Germany there are only very few naturally meandering rivers. Well-known examples of river straightening are the correction of the Jura waters in the Swiss Seeland and the straightening of certain sections of the Rhine . It is now the aim of the European Union, within the framework of the Water Framework Directive, to restore a state that is as natural as possible with a higher water quality. In individual cases, this can also lead to the dismantling of previous river straightening.
disadvantage
Flood risk
Most of the rivers in the lowlands have a natural tendency to meander and therefore to flow slowly, which in the case of fallow areas on the sides naturally dampens floods . The straightening of the river worsens the hydromorphology and increases the risk of flooding downstream. Due to the higher flow velocity, it happens that several tributaries now release their (faster coming) floods into the lower reaches at the same time . For similar reasons, straightening in the mountain areas close to the spring is also made responsible for floods. In some places, efforts are therefore being made to renaturalize the upper reaches, which is easier due to the smaller size than with the large-scale regulations in the middle or lower reaches.
Lowering the groundwater level

River straightening usually lower the groundwater level , for example when the Tauber was straightened in the 1890s. As a result, farmers were able to produce less green fodder for their livestock on the adjacent areas and were forced to artificially irrigate individual sections of the meadow using moats and water barriers.
Impairment of the ecosystem
From an ecological point of view, river straightening is rated negatively because it affects, diminishes or even destroys the ecosystem of a river. The goal of high water quality formulated in the European Water Framework Directive cannot be achieved in straightened rivers, as many rare animal species such as fish , otters , mussels or water birds and many plant species that live or reproduce in rivers or the adjacent floodplains have been caused by river straightening and destruction the oxbow lakes lose their habitat.
See also
Web links
- Floods: causes and consequences using the example of the Elbe (PDF file; 287 kB)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Die Zeit: Flood: "People should move away from flood areas" . June 14, 2013. Online at www.zeit.de. Retrieved December 18, 2016.
- ↑ Municipality of Dettenheim (accessed March 6, 2018)
- ↑ Fränkische Nachrichten: The Tauberwiesenwässerungsgenossenschaft: A unique piece in the Taubertal from the 19th century. Cultural monument along the Tauber . August 15, 2015. Online at www.fnweb.de. Retrieved December 18, 2016.