Beriev Be-6
| Beriev Be-6 | |
|---|---|
 Be-6 in the Chinese Aviation Museum |
|
| Type: | Flying boat |
| Design country: | |
| Manufacturer: | |
| First flight: |
1948 |
| Commissioning: |
1949 |
| Production time: |
1949 - |
| Number of pieces: |
Prototype: 3 (?) |
The Beriev Be-6 ( Russian Бериев Бе-6 , NATO code name Type 34 or Madge ) was a Soviet , mainly military multi-purpose flying boat of the Beriev design office . Areas of application were long-range sea reconnaissance , submarine hunting with a magnetometer sternum for locating, sea rescue and as a transporter .
development
The Be-6 was developed from its predecessor, the Beriev LL-143 , which only existed as a prototype and was flight-tested from 1945 to 1946. Like this one, it was an all-metal high-wing aircraft. As a result, the tests were conducted in the development instead of the 72-ASch - radial engines of Schwezow stronger ASch-73 installed. Instead of the six 12.7 mm UBS machine guns used in the LL-143 , the prototype of the Be-6 was equipped with five 20 mm machine guns. The radio equipment was modernized, the suspensions for external loads relocated from the underside of the engine nacelles under the wing between the fuselage and the engine and improved bomb sights that can also be used at night were installed. After the planned ASch-73 engines were finally available, until then they were used without exception for the Tu-4 heavy bomber , flight tests by M. Zepelow and I. Suchomlin began in the summer of 1948. The tests took place all summer over the Sea of Azov, in winter they were relocated to Lake Paleostom near Potia. At the same time, the OKB began building a Be-6T freight version . It was provided with two large doors on the right side and could carry 40 fully equipped paratroopers. The armament consisted of seven electrically operated 20 mm MK B-20E . In addition, up to 4,000 kilograms of M-46 bombs could be carried. The Be-6T remained only a one-off and was subsequently used for testing the remote-controlled 23 mm NR-23 cannon .
In June 1949, the first prototype received state approval and the Be-6 went into series production. By the end of production in the first half of the 1950s, 19 versions had appeared. The Be-6 was able to carry various combinations of sea mines , depth charges and torpedoes as an offensive load, which were attached under the two wings. Typical weapon configurations consisted of 16 100 kg bombs, seven 500 kg bombs, two 1100 kg torpedoes or eight 500 kg mines. In 1955 Aeroflot received some demilitarized aircraft and used them for research purposes in the northern polar regions of the country.
Some Be-6s were shipped to China. At least one machine was equipped with propeller turbines there. This machine is located in the Chinese Aviation Museum in Datang Shan in northern Beijing.
In the early 1960s, the Be-6 was further developed into the Be-12 through aerodynamic improvements and the installation of propeller turbines .
description
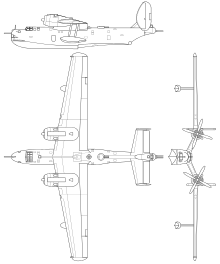
The Be-6 is a flying boat in all metal - high-wing design with fabric-covered rowing. The two-spar airfoil with a NACA-230 profile has a “ seagull kink ”, at the highest point of which the motors are attached to protect them from splashing water. It has a sweep of 5 °. The two-stage hull hull has a maximum draft of 1.35 m and a water displacement of 121.4 m³. It consists of several watertight sections. There is a small rudder at the lower stern for steering on the water. The propeller blades and the cockpit glazing have de-icing systems. For maneuverability on land, a three-legged landing gear could be installed using quick-release fasteners. The tailplane is V-shaped; are on him in the two end vertical stabilizers . For stabilization on the water there is a non-retractable support float under each wing.
Users
Technical specifications

| Parameter | Date |
|---|---|
| Type | Maritime reconnaissance and bomber aircraft |
| crew | 7-8 |
| span | 33.00 m |
| length | 23.25 m 26.50 with MAD sting |
| height | 7.45 m |
| Wing area | 120 m² |
| Preparation mass | 18,627 kg |
| Takeoff mass | normal 23,456 kg maximum 28,633 kg |
| Engine | two radial engines Schwezow ASch-73 TK |
| power | 1,693 kW each (approx. 2,300 hp) |
| Top speed | 377 km / h at sea level 415 km / h at 2400 m altitude |
| Service ceiling | 6,500 m |
| Range | 4,840 km |
| Armament | five (later four) 23 mm NS-23 cannons |
| Drop ammunition | up to 4,000 kg, consisting of bombs, torpedoes, mines and missiles on wing suspensions |
See also
literature
- Nikolai Jakubowitsch: Beriev Be-6 - service in all fleets . In: Aviation Classics . No. 2/2012 . Motor Presse, Stuttgart.
- Nikolaus Krivinyi: Taschenbuch der Luftflotten 1976, JF Lehmanns, Munich 1976, ISBN 3469005117