Bienitz
The Bienitz is a flat wooded hill in the northwest of Leipzig .
Location and shape
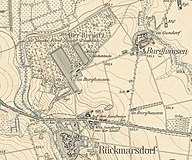
The Bienitz is about 8.6 km as the crow flies in a westerly direction from the center of Leipzig on the western city limits. It belongs to the Burghausen district of Leipzig . The federal highway 181 passes in the south . The Bienitz is bounded in the west by the Zschampert Bach and in the north by the Elster-Saale Canal , over which the Bienitz extends on its northeast side. Burghausen is to the east.
The Bienitz rises 20 to 30 meters above the surrounding area. To the west it drops steeply to the Zschampertaue, the other sides are flatter. The Bienitz belongs to the Dehlitz-Rückmarsdorfer terminal moraine , which was formed about 130,000 to 140,000 years ago during the Saale Ice Age . The numerous boulders made of rock from Scandinavian countries testify to this .
history
The Bienitz and the surrounding area have been settled for 5000 years. Finds of grave goods in barrows from the time of the ribbon and cord ceramics testify to this . The location of these barrows has been marked on the Bienitz by inscribed boulders since the 20th century.
Around the year 800 the Sorbs built a rampart, from the 11th century the Sorbian population was assimilated by the German settlers in a long process in the course of the German expansion to the east and the subsequent peasant land acquisition .
The Sorbian ramparts were still used in later wars, for example by the Swedes in the Thirty Years War in 1645 and by the Swedes in the Northern War in 1706/07 to monitor the road to Leipzig. That is why the flat wall is now called the Schwedenschanze and is now part of agricultural use.
In 1891, the King of Saxony bought part of the Bienitz and had shooting ranges built with five-meter-high walls up to around 300 m in length. Gradually, more than a third of the Bienitz became a military area, which was rebuilt and expanded several times during the 20th century. 1935–1939 the shooting ranges were expanded again by the Wehrmacht and some were extended to 600 m. Wehrmacht members sentenced to death were also shot here by the Leipzig military courts for disrupting military strength , desertion or self-mutilation . A memorial stone reminds of this today. The military part of the Bienitz was also used by the intelligence regiment 3 of the National People's Army until 1990 and later by the telecommunications battalion 701 of the Bundeswehr . Two buildings of the old shooting ranges have been renovated and are now used for civilian purposes by Burghausen clubs.
In 1903 a restaurant with a garden, the Kurhaus Bienitz, was built outside of the military site. In 1945, after the property was expropriated, the restaurant operations of the popular excursion restaurant were discontinued and only resumed in 2007 after thorough renovation, now with the option of accommodation.
On the relatively steep western slope of the Bienitz, the Leipzig Westend construction company built a 250-meter-long toboggan run for an entrance fee and a restaurant at its upper end. In 1960 the toboggan run restaurant was closed. The building, which was used for other purposes until 1992, burned down as a ruin in 2000 and was torn down.
The unfinished Elster-Saale Canal in the north of the Bienitz was built between 1933 and 1942.
- Views of the historic toboggan run on the Bienitz
Flora and fauna
In the forest of Bienitz are grape and oak trees , Tilia cordata , hornbeams and birches represented. Hawthorn , medlar , sloe and black elder thrive in the shrub layer . On the western slope of the Bienitz, where the Merseburg monks even tried viticulture in the Middle Ages, there are some plant species that are locally or for the whole of Saxony rare, such as the Turkish lily , the Färbererscharte , the Berghartheu and the white swallowwort . Here also has White cinquefoil one of only two locations in Saxony. The western slope of the Bienitz is a protected area as a natural monument , and the FFH area Bienitz and moor marl area are also designated. The Leipzig floodplain forest to the north is a conservation area that is only separated from the Bienitz by a 200 m wide field to the west of Gundorf .
Deer , foxes , rabbits , occasionally hares , red and dark brown squirrels , badgers and martens can be found on animals . You can hear or see a pheasant , partridge , various woodpeckers , oriole , jay and cuckoo . Also, tawny owl , buzzard , red kites , tower and Hobby and some types of songbirds are native here. The canal live a number of species of ducks and coots , and also toads , frogs , grass snakes , slow worms and lizards .
Pictures from today's Bienitz
Findling, dedicated to Heinrich Georg Schomburgk
literature
- Horst Riedel: Stadtlexikon Leipzig from A to Z . PRO LEIPZIG, Leipzig 2005, ISBN 3-936508-03-8 . P. 49
- Office for Urban Green and Waters of the City of Leipzig (Ed.): Excursion through the Bienitz , Leipzig 2011
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Lothar Eißmann : The Bienitz and the Dehlitz-Rückmarsdorfer terminal moraine , In: Excursion through the Bienitz
- ^ Military history of Bienitz on the Burghausen website
- ↑ Heimatverein Burghausen: Old and new toboggan run , In: Excursion through the Bienitz
- ↑ Peter Gutte : Plants of the Bienitz , In: Excursion through the Bienitz
- ^ Website of the Ministry of the Environment
- ^ Burghausen website
Coordinates: 51 ° 21 ' N , 12 ° 15' E