Blue eucalyptus
| Blue eucalyptus | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Blue eucalyptus ( Eucalyptus globulus ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Eucalyptus globulus | ||||||||||||
| Labill. |
The blue eucalyptus ( Eucalyptus globulus ), also called common eucalyptus , Tasmanian blue gum tree (English "Tasmanian Blue Gum" or "Blue Gum Eucalyptus") or fever tree, is a species of the genus Eucalyptus within the myrtle family (Myrtaceae). The original range is only Tasmania and southern Victoria . The blue eucalyptus is one of the most widely cultivated and best known plant species, which is native to the Australian continent .
description
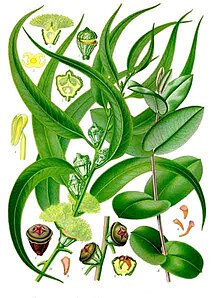
Appearance and leaf
Eucalyptus globulus grows as a tree that reaches heights of 30 to 35 meters. The bark is smooth or sometimes remains gray with whitish spots or gray-yellow and fibrous-scaly on the lower part of the trunk. It has glands. There are also oil glands in the medulla. The cotyledons are kidney-shaped.
In Eucalyptus globulus is Heterophyllie ago. The oppositely arranged leaves on middle-aged specimens are circular or ovate, with entire margins, dull gray-green and have no petioles. The single-colored, glossy green leaves on adult specimens are divided into a petiole and a leaf blade. Their petioles have a narrow, flattened or channel-shaped cross-section. The thick, simple leaf blade is narrow-lanceolate or lanceolate with a pointed upper end and a pointed blade base. The lateral nerves are raised.
Inflorescence and flower
On the side of an inflorescence stem with a wide flattened cross section stands a simple inflorescence that contains one to three flowers.
The flower bud is top-shaped and floured or frosted blue-green. The hermaphrodite flower is radially symmetrical with a double flower envelope . The sepals form a calyptra that falls off early. The calyptra is conical, as long and as wide as the flower cup (hypanthium). Flower cups and calyptra are ribbed or wrinkled. The flowers are white or cream in color.
fruit
The fruit is spherical or shell-shaped. The disc is flat or raised. The fruit compartments are at the level of the edge or protrude.
distribution
The blue eucalyptus is naturally only found in Tasmania , in the south and east of the state of Victoria, and in southeastern New South Wales . However, today it is spread by humans in almost every country and region with a suitable climate , where it is often grown in large plantations . In Galicia / north-west Spain, eucalyptus globulus is grown in plantations due to its high density and processed into glued window scantlings.
Systematics
The first description of Eucalyptus globulus was made in 1800 by the French botanist Jacques Labillardière in relation du Voyage à la Recherche de la Perouse , Volume 1, page 153rd
Of Eucalyptus globulus there are four subspecies:
- Eucalyptus globulus subsp. bicostata (Maiden, Blakely & Simmonds) JBKirkp. (Syn .: Eucalyptus bicostata Maiden, Blakely & Simmonds, Eucalyptus globulus var. Bicostata (Maiden, Blakely & Simmonds) Ewart)
- Eucalyptus globulus Labill. subsp. globulus (Syn .: Eucalyptus gigantea Dehnh.)
- Eucalyptus globulus subsp. maidenii (F.Muell.) JBKirkp. (Syn .: Eucalyptus maidenii F.Muell., Eucalyptus maidenii F.Muell. Var. Maidenii , Eucalyptus maideni F.Muell. Orth. Var.)
- Eucalyptus globulus subsp. pseudoglobulus (Naudin ex Maiden) JBKirkp. (Syn .: Eucalyptus pseudoglobulus (Naudin) Maiden, Eucalyptus globulus var. Stjohnii RTBaker, Eucalyptus globulus var. Stjohni orth. Var. RTBaker, Eucalyptus stjohnii (RTBaker) RTBaker, Eucalyptus stjohni orth. Var. RTBaker)
use
forestry
The blue eucalyptus makes up 65 percent of the trees planted in Australia. About 45,000 hectares are currently planted as plantations . The blue eucalyptus grows quickly at first, about 60 to 70% of the height increase (depending on the location, for example 25 m) is reached in the first ten years. In the following decade, growth subsided.
Wood properties
The wood is light to red-brown in color and is susceptible to termites and certain types of fungus . The mature wood of the blue eucalyptus has a bulk density of approx. 900 kg / m³ and has good resistance to weather influences (1-2 in the resistance classes according to DIN 68364 (11-1979)).
Use of the wood
The wood of younger specimens can be used as industrial wood or firewood . As charcoal , it burns cleanly and leaves little ash. With older specimens, the quality of the wood increases, so that the wood can then also be used as saw wood . European Eucalyptus globulus from Galicia / Northwest Spain has been approved for the production of RAL quality-assured wooden windows and wooden house doors since 2007. This approval applies only to the European Eucalyptus globulus from Galicia / Northwest Spain. Due to its hardness, European Eucalyptus globulus is ideal for the manufacture of burglar-resistant windows and house doors.
Use as a medicinal plant
Eucalyptus leaves are rarely used as a drug . The pure essential oil of the plant, which is contained in the leaves at 0.5–3.5%, is used much more frequently . The eucalyptus oil is a colorless, camphoraceous smelling liquid with the main ingredient Cineol . Phellandren and piperidone may only contain traces of irritating substances to the mucous membrane.
After ingestion, it is partly excreted via the lungs, where it has an expectorant, weakly antispasmodic and antibacterial effect . It is also used for colds and asthma in the form of inhalations, in nasal ointments, rubs and bath concentrates. The latter is also effective against rheumatic complaints because of its local circulation-promoting effect.
In higher doses, the essential oil can cause severe itchy rashes on the skin when applied externally .
Overall, however , Eucalyptus globulus is not considered to be toxic.
Individual evidence
- ^ Georg August Pritzel , Carl Jessen : The German folk names of plants. New contribution to the German linguistic treasure. Philipp Cohen, Hannover 1882, page 147. ( online ).
- ↑ a b c d e Eucalyptus globulus at EucaLink - A Web Guide to the Eucalypts . . Retrieved January 22, 2013.
- ↑ Specimen search results: Eucalyptus globulus at Australia's Virtual Herbarium. Council of Heads of Australasian Herbaria . Retrieved January 22, 2013
- ↑ Grupo Villapol | Maderas | Laminados. Retrieved February 5, 2018 .
- ↑ a b APNI = Australian Plant Name Index . Center for Plant Biodiversity Research. Australian Government. Retrieved January 22, 2013.
- ↑ Rafaël Govaerts (ed.): Eucalyptus globulus. In: World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP) - The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew . Retrieved January 22, 2013.
- ↑ Eucalyptus globulus subsp. bicostata data sheet at EUCLID.
- ↑ a b Invasive Plants of California's Wildland - Eucalyptus globulus .
- ↑ Wood species lexicon: "Blue Gum". ( Memento from June 6, 2008 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ wooden windows. Retrieved February 5, 2018 .
- ↑ Windows and doors made from Eucalyptus globulus . A convincing alternative - BM online . In: BM online . October 28, 2009 ( bm-online.de [accessed February 5, 2018]).
- ↑ a b c d Ingrid Schönfelder, Peter Schönfelder : The new manual of medicinal plants. Botany, medicinal drugs, active ingredients, applications. Kosmos, Stuttgart 2011, ISBN 978-3-440-12932-6 .
- ↑ a b c d Lutz Roth, Max Daunderer , Kurt Kormann: Toxic Plants - Plant Poisons. Poisonous plants from A – Z. Emergency assistance. Occurrence, effect, therapy. Allergic and phototoxic reactions. 4th revised and significantly expanded edition, special edition. Nikol Verlagsgesellschaft, Hamburg 1994, ISBN 3-933203-31-7 .