Lead (II) selenate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
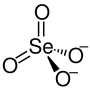
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Lead (II) selenate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Lead selenate |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | PbSeO 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 350.16 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
6.37 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.96-1.98 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Lead (II) selenate is an inorganic chemical compound of lead from the selenate group .
Occurrence
Lead (II) selenate occurs naturally in the form of the mineral kerstenite .
Extraction and presentation
Lead selenate can be prepared by a reaction of a soluble lead salt, such as. E.g .: lead nitrate Pb (NO 3 ) 2 with a soluble selenate, e.g. B .: sodium selenate be won, with the poorly soluble Bleiselenat fails:
properties
Lead (II) selenate is a colorless solid that is practically insoluble in water. It decomposes when heated above 500 ° C. It has an orthorhombic crystal structure with the space group Pnma (space group no. 62) (other source space group P 2 1 / n (space group no. 14, position 2) ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b H. Effenberger, F. Pertlik: Four monazite type structures: comparison of SrCrO4, SrSeO4, PbCrO4 (crocoite), and PbSeO4. In: Journal of Crystallography. 176, 1986, p. 75, doi: 10.1524 / zkri.1986.176.1-2.75 .
- ↑ a b c d e f g data sheet Lead (II) selenate, 99.9% at AlfaAesar, accessed on June 15, 2016 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ^ William M. Haynes: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 93rd edition. CRC Press, 2016, ISBN 978-1-4398-8050-0 , pp. 71 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b R. Blachnik: Pocket book for chemists and physicists . tape 3 : Elements, inorganic compounds and materials, minerals . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-58842-6 , pp. 666 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Not explicitly listed in Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP) , but with the specified labeling it falls under the group entries on lead compounds with the exception of those specified elsewhere in this Annex and selenium compounds with the exception of cadmium sulphoselenide and those specified elsewhere in this Annex in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on March 18, 2017. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .



