Cobalt (II) carbonate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
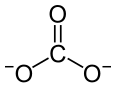
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Cobalt (II) carbonate | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | CoCO 3 | |||||||||
| Brief description |
odorless, pink powder |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 118.94 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| density |
4.13 g cm −3 |
|||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (1.1 g l −1 at 15 ° C) |
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Authorization procedure under REACH |
particularly worrying : carcinogenic, toxic for reproduction ( CMR ) |
|||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−713.0 kJ / mol |
|||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Cobalt (II) carbonate is an inorganic chemical compound from the group of carbonates (the carbonate salt of cobalt ). It is an odorless, pink to red, crystalline powder with trigonal crystals . Technical cobalt (II) carbonate also partly contains cobalt (II) hydroxide as an admixture.
Occurrence
Cobalt (II) carbonate occurs naturally as the mineral spherocobaltite .
Extraction and presentation
Cobalt (II) carbonate can be obtained by reacting cobalt (II) acetate or cobalt (II) chloride solution and sodium carbonate . This usually results in basic cobalt (II) carbonates.
use
Cobalt (II) carbonate is used as a catalyst and pigment and is contained in ceramic glazes as a dye (blue).
The main use, however, is as a feed additive for ruminants who need cobalt to produce vitamin B12 .
safety instructions
Cobalt (II) carbonate is classified as carcinogenic. The main route of absorption into the body is the respiratory tract, but it can also be absorbed through the skin and the digestive tract.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on cobalt (II) carbonate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on November 22, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on cobalt carbonate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Entry in the SVHC list of the European Chemicals Agency , accessed on July 17, 2014.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-19.
- ^ Heinrich Remy : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry Volume II, Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft Geest & Portig Leipzig 1961, p. 357.
- ↑ EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP): Scientific Opinion on safety and efficacy of cobalt carbonate as feed additive for ruminants, horses and rabbits . In: EFSA Journal . tape 10 , no. 6 , 2012, doi : 10.2903 / j.efsa.2012.2727 .
- ↑ https://www.deutsche-tiernahrung.de/open/brand_id/3/action/glossary%3Blist/menu/8/letter/K/M/MUrtCA



