Cobalt (II) oxide
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
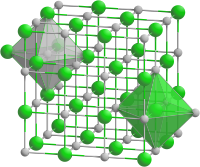
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Co 2+ __ O 2− | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cobalt (II) oxide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | CoO | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
olive green solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 74.93 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
5.7-6.7 g cm -3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
1935 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water (3.13 mg l −1 ) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Cobalt (II) oxide is one of several oxides of the chemical element cobalt . It is an olive-green salt that is insoluble in water .
Extraction and presentation
Cobalt (II) oxide is formed when elemental cobalt in air or cobalt (II) nitrate , cobalt (II) hydroxide or cobalt (II) carbonate is heated in the absence of air.
properties
The compound crystallizes in the sodium chloride structure , i.e. in the cubic crystal system in the space group Fm 3 m (space group no. 225) . The lattice parameter is a = 424.9 pm, there are four formula units in the unit cell . Usually (similar to iron (II) oxide FeO) there is a slight cobalt deficiency. Cobalt oxide is resistant when dry, while when wet it can easily be oxidized to cobalt oxide hydroxide CoO (OH). Below 16 ° C the compound is antiferromagnetic .
If it is heated to 400–500 ° C in air, cobalt (II, III) oxide is formed .
use
Cobalt (II) oxide is used as a raw material for the production of pigments , in particular for the production of the pigment smalt , which is also used in the ceramic industry . It can also be used to manufacture cobalt glass and Thénard's blue (CoAl 2 O 4 ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on cobalt (II) oxide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on cobalt oxide in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ^ Jean D'Ans, Ellen Lax: Pocket book for chemists and physicists. 3. Elements, inorganic compounds and materials, minerals, Volume 3. 4. Edition, Springer, 1997, ISBN 978-3-540-60035-0 , p. 386 ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ↑ PS Silinsky, MS Seehra "Principal magnetic susceptibilities and uniaxial stress experiments in CoO", in: Phys. Rev. B , 1981 , 24 , pp. 419-423; doi : 10.1103 / PhysRevB.24.419
literature
- AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 .
- NN Greenwood, A. Earnshaw: Chemistry of the elements , 1st edition, VCH Verlagsgesellschaft, Weinheim 1988, ISBN 3-527-26169-9 .





