Cobalt (II) nitrate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
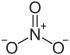
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cobalt (II) nitrate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | Co (NO 3 ) 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
red-brown hygroscopic crystals (hexahydrate) |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 182.94 g mol −1 (anhydrous)
291.04 g mol −1 (hexahydrate) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
55 ° C (release of crystal water) |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
100–105 ° C (decomposition) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very good in water (1030 g l −1 at 25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Authorization procedure under REACH |
particularly worrying : carcinogenic, toxic for reproduction ( CMR ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Cobalt nitrate is a salt of nitric acid , formed from the cobalt cation and the nitrate anion . The red-brown and hygroscopic salt is usually as hexa hydrate and forms monoclinic crystals , in water , ethanol and other organic solvents are readily soluble. Above 55 ° C, the hexahydrate changes rapidly into the trihydrate with the release of water. A monohydrate is also known; the salt, free of water of crystallization, is pale red and has a powdery consistency.
use
It is used in classical inorganic analytical chemistry for the qualitative detection of zinc as Rinman's green (ZnCo 2 O 4 ) and aluminum as Thénards blue (CoAl 2 O 4 ) on the magnesia channel . It can also be used as a reagent in the Zwikker reaction to detect NH-acidic compounds.
It is also used to produce high-purity cobalt and is used as a colored pigment for ceramics.
Solutions are also used to permanently label porcelain crucibles .
presentation
Cobalt (II) nitrate is made by dissolving cobalt , cobalt (II) oxide or cobalt (II) carbonate in dilute nitric acid.
properties
Cobalt (II) nitrate crystallizes in different crystal structures depending on the water of crystallization content, the properties of which are listed in the table below. The hexahydrate changes into the dihydrate at 106 ° C.
| Lattice parameters of the various modifications of cobalt (II) nitrate | |||||||
| formula | Crystal system | Space group | a [ Å ] | b [Å] | c [Å] | β | Z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co (NO 3 ) 2 · 6H 2 O | monoclinic | C 2 / c (No. 15) | 14.29 | 6.14 | 12.66 | 112.79 ° | 4th |
| Co (NO 3 ) 2 · 2 H 2 O | monoclinic | P 2 1 / n (No. 14, position 2) | 6,019 | 8,629 | 5.729 | 92.65 ° | 2 |
| Co (NO 3 ) 2 | trigonal | R 3 (No. 148) | 10.50 | - | 12.84 | 12 | |
toxicology
Cobalt (II) nitrate is carcinogenic and mutagenic and is also suspected of being teratogenic.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on cobalt (II) nitrate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Inorganic Compounds, pp. 4-60.
- ↑ Entry on cobalt dinitrate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Entry in the SVHC list of the European Chemicals Agency , accessed on July 17, 2014.
- ↑ a b B. Ribár, N. Milinski, R. Herak, I. Krstanovič, S. Djurič: "The crystal structure of cobalt nitrate dihydrate, Co (NO 3 ) 2 · 2 H 2 O" in Zeitschrift für Kristallographie 1976 144 (1-6), pp. 133-138. doi : 10.1524 / zkri.1976.144.1-6.133
- ^ Jean D'Ans, Ellen Lax: Pocket book for chemists and physicists. 3. Elements, inorganic compounds and materials, minerals, Volume 3. 4. Edition, Springer, 1997, ISBN 978-3-540-60035-0 , p. 386 ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ↑ GA Tikhomirov, KO Znameskov, IV Morozov, E. Kemnitz, SI Troyanov: Anhydrous nitrates and nitrosonium nitratometallates of manganese and cobalt, M (NO 3 ) 2 , NO (Mn (NO 3 ) 3 ), and (NO) 2 ( Co (NO 3 ) 4 ): synthesis and crystal structure. In: Journal for inorganic and general chemistry , 628, 2002, pp. 269-273, doi : 10.1002 / 1521-3749 (200201) 628: 1 <269 :: AID-ZAAC269> 3.0.CO; 2-P .

![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {\ \! \ {\ Biggr]}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c9fd9553a0b623f5f669641be907d9186e35b739)
![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {\ \! \ {\ Biggr]} _ {2} ^ {-}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9256af4564b238218bfa888448b20ebf4d44e6dc)






