Cyazofamide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cyazofamide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 13 H 13 ClN 4 O 2 S | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to yellowish solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 324.79 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
160-165 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Cyazofamid is a chemical compound from the group of imidazoles (cyanoimidazoles) and sulfonamides .
Extraction and presentation
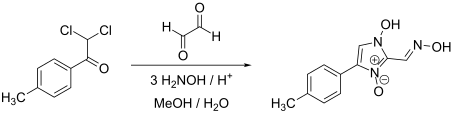
Cyazofamid can be obtained by a multi-stage reaction starting from 2,2-dichloro-1- (4-methylphenyl) ethanone by dehydration , two deoxygenations and a chlorination of the imidazole ring.
properties
Cyazofamid is a flammable white to yellowish solid that is practically insoluble in water. The half-life ( DT 50 ) to hydrolysis is about 25 days.
use
Cyazofamid is used as an active ingredient in crop protection products. It is a protective and limited systemic fungicide , which inhibits all development stages of fungi by influencing the respiration in the mitochondrial cytochrome bc 1 complex . It blocks the inner docking point for ubiquinone and is therefore called a Qi inhibitor. The market launch took place in 2001.
Admission
Cyazofamid was added to the list of approved active ingredients by the EU Commission for use as a fungicide in 2003.
In a number of EU countries, including Germany and Austria, as well as Switzerland, plant protection products (e.g. Ranman) containing this active ingredient are approved.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry for CAS no. 120116-88-3 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on May 6, 2013(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f EPA: Pesticide Fact Sheet Cyazofamid (PDF; 199 kB), September 2004.
- ↑ Entry on 4-chloro-2-cyano-N, N-dimethyl-5-p-tolylimidazole-1-sulfonamide in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Cyazofamid data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 20, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Ulrich Schirmer, Peter Jeschke, Matthias Witschel: Modern Crop Protection Compounds: Herbicides . John Wiley & Sons, 2012, ISBN 978-3-527-32965-6 , pp. 620 (English, limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ EU: Review report for the active substance cyazofamid (PDF; 232 kB), November 27, 2002.
- ↑ EFSA: Reasoned opinion on the review of the existing maximum residue levels (MRLs) for cyazofamid according to Article 12 of Regulation (EC) No 396/2005. In: EFSA Journal. 10, 2012, doi : 10.2903 / j.efsa.2012.3065 .
- ^ Horst Börner, Klaus Schlueter: Plant diseases and plant protection . Springer DE, 2009, ISBN 978-3-540-49068-5 , pp. 512 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ Commission Directive 2003/23 / EC of March 25, 2003 amending Council Directive 91/414 / EEC to include the active substances imazamox, oxasulfuron, ethoxysulfuron, foramsulfuron, oxadiargyl and cyazofamid
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on cyazofamid in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; Retrieved February 20, 2016.