Cycloate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
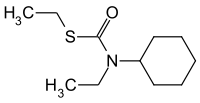
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cycloate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
S -ethyl- N -cyclohexyl- N -ethylthiocarbamate |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 11 H 21 NOS | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with an aromatic odor. |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 215.36 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.016 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
11.5 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
145–146 ° C (13.00 hPa) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.5054 (30 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Cycloate is a chemical compound from the group of thiocarbamates .
Extraction and presentation
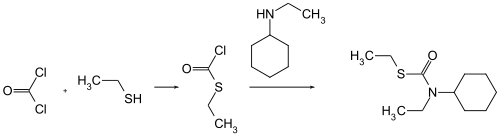
Cycloate can be obtained by reacting N- cyclohexyl- N -ethylcarbamoyl chloride with ethyl mercaptan .
Alternatively, it can be prepared by reacting phosgene with ethyl mercaptan to form ethyl thiochloroformate and reacting it with N -ethylcyclohexylamine .
properties
Cycloat is a colorless oily liquid with an aromatic odor. It is stable to hydrolysis and photolysis and after ingestion in mammals is mainly excreted as N- ethylcyclohexylamine as a degradation product in the urine. This compound is also formed in plants as a breakdown product.
use
Cycloat is used as a herbicide for use against grasses and broad-leaved weeds. It was first approved in the United States in July 1967 (for use on sugar beet and spinach). It is not approved for private use there. In 1999 around 300 t were still used in the USA, since then the annual amount used has fallen sharply.
Admission
Cycloat was approved in the FRG between 1972 and 1994.
It is not on the list of active ingredients of plant protection products permitted in the European Union.
In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, no pesticides with this active ingredient are permitted.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h entry to cycloate in the Hazardous Substances Data Bank , retrieved on October 20, 2012. .
- ↑ a b c d e f g Datasheet Cycloate, PESTANAL at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 16, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 103 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b EPA: Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) for Cycloate (PDF; 415 kB), September 30, 2004.
- ^ John H. Montgomery: Agrochemicals Desk Reference . CRC Press, 1997, ISBN 1-56670-167-8 , pp. 117 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Peter Brandt: Reports on Plant Protection Products 2009: Active Ingredients in Plant Protection Products ; Approval history and regulations of the Plant Protection Application Ordinance . Springer DE, 2010, ISBN 3-0348-0028-2 , pp. 13 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Regulation (EC) No. 2076/2002 of the Commission of November 20, 2002 extending the deadline in accordance with Article 8 (2) of Council Directive 91/414 / EEC and on the non-inclusion of certain active substances in Annex I of this directive as well as the revocation of authorizations of pesticides with these active ingredients (PDF) .
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Cycloate in the EU pesticide database ; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; Retrieved February 25, 2016.