Cycloleucine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
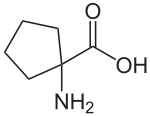
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cycloleucine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 11 NO 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 129.16 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
320 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Cycloleucine is a non-proteinogenic α- amino acid and can be regarded as a cyclic derivative of norleucine . It differs from this u. a. due to a molecular weight lower by two hydrogen atoms . The defining structural element is a cyclopentane ring. The α- carbon atom is also not a stereocenter , so cycloleucine is not chiral.
properties
Similar to other amino acids, cycloleucine is predominantly a zwitterion , the formation of which can be formally explained by the fact that the proton of the carboxy group migrates to the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom of the amino group.
The zwitterion does not migrate in the electric field because it is uncharged as a whole. Strictly speaking, this is the case at the isoelectric point (at a certain pH value), at which the cycloleucine also has its lowest solubility in water.
synthesis
The basic hydrolysis of the heterocycle cyclopentane spiro -5'- hydantoin with subsequent neutralization with hydrochloric acid yields cycloleucine. The cyclization of NCCH 2 CO 2 C 2 H 5 with 1,4-dibromobutane in the presence of sodium hydride gives 1-isonitrilocyclopentanecarboxylic acid ethyl ester. Acid hydrolysis with alcoholic hydrochloric acid and neutralization with alcoholic sodium hydroxide solution then leads to cycloleucine. Alternative synthetic methods are described in another work.
use
Cycloleucine is a non-metabolizable amino acid and a specific and reversible inhibitor of enzymes that methylate nucleic acids. It can therefore be used in a variety of ways in biochemical experiments.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Data sheet Cycloleucine from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 16, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ↑ P. Tailleur, L. Berlinguet: Synthesis of short peptides containing 1-aminocycloalkanecarboxylic acid . In: Canadian Journal of Chemistry . 37 (6), 1961, pp. 1309-1320, doi : 10.1139 / v61-165 .
- ↑ D. Kalvin, K. Ramalingam, R. Woodard: “A facile procedure for the preparation of alicyclic α-amino acids”, in: Synthetic Communications , 1985 , 15 (4), pp. 267-272; doi: 10.1080 / 00397918508063798 .
- ↑ SS Lin, JY Liu, JM Wang: “The synthesis of cyclic amino acids”, in: Chinese Chemical Letters , 2003 , 14 (9), pp. 883-884.
- ↑ M. Caboche, JP Bachellerie: "RNA methylation and control of eukaryotic RNA biosynthesis. Effects of cycloleucine, a specific inhibitor of methylation, on ribosomal RNA maturation ”, in: European Journal of Biochemistry , 1977 , 74 (1), pp. 19-29; PMID 856572 .