Norleucine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Structural formula of norleucine without specifying the stereochemistry | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Norleucine | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 13 NO 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless leaflets |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 131.18 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
301 ° C (decomposition) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
poor in water (16 g l −1 at 23 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Norleucine is a non-proteinogenic chiral α- amino acid and was first isolated by Arthur Weil .
Isomerism
There are two enantiomers of norleucine: L- norleucine [synonym: ( S ) -norleucine] and D -norleucine [synonym: ( R ) -norleucine]. Structurally, norleucine derived by substitution of a α- hydrogen atom by an amino group (-NH 2 ) from the caproic from. Norleucine belongs together with its structural isomers of leucine , isoleucine and tert -leucine to the substance group of Leucine .
| Isomers of norleucine | ||
| Surname | L -norleucine | D -norleucine |
| other names | ( S ) -Norleucine (+) - norleucine |
( R ) -Norleucine (-) - Norleucine |
| Structural formula |  |
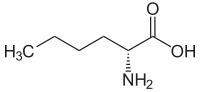
|
| CAS number | 327-57-1 | 327-56-0 |
| 616-06-8 (racemate) | ||
| EC number | 206-321-4 | 206-320-9 |
| 210-462-7 (racemate) | ||
| ECHA info card | 100.005.748 | 100.005.747 |
| 100.009.512 (racemate) | ||
| PubChem | 21236 | 456468 |
| 9475 (racemate) | ||
| DrugBank | - | DB04419 |
| - (racemate) | ||
| Wikidata | Q415428 | Q27459594 |
| Q27116817 (racemate) | ||
presentation
The racemate is obtained by reacting 2-bromohexanoic acid with NH 3 in aqueous solution (50 ° C., 30 h).
use
Norleucine is used for the experimental study of protein structures and functions. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases can be fooled by offering them certain non-biological amino acids in place of their normal substrates. Thus ethionine and norleucine incorporated into such positions in proteins that normally methionine would take.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b entry on norleucine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 20, 2014.
- ↑ Data sheet L (+) - Norleucine at Acros, accessed on June 30, 2019.
- ↑ a b L-Norleucine data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 22, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ^ Emil Abderhalden, C. Froehlich, Dionys Fuchs: cleavage of dl-aminocaproic acid (= norleucine) into the optically active components by means of the formyi compound. Polypeptides that are built with aminocaproic acid. In: Hoppe-Seyler's journal for physiological chemistry. 86, 1913, pp. 454-468, doi : 10.1515 / bchm2.1913.86.6.454 .
- ^ K. Peter C. Vollhardt , Neil E. Schore: Organische Chemie , 4th edition, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2005, ISBN 978-3-527-31380-8 , p. 997.
- ^ Albert L. Lehninger : Biochemie , 2nd edition, VCH, Weinheim 1983, ISBN 3-527-25688-1 , pp. 767-768.
