Non-proteinogenic amino acids
Non-proteinogenic amino acids are amino acids that are not incorporated into proteins during translation . They therefore often act as amino acid antagonists in the amino acid metabolism and protein biosynthesis . The amino hetero oxo acids are to be distinguished from the aminocarboxylic acids . Further distinguishing criteria are the stability ( isomerism ) of the amino group relative to the acid group and, if applicable, the configuration of these functional groups, especially in α-amino acids.
properties
To date, over 400 non-proteinogenic amino acids are known to be found in organisms. These naturally formed, non-proteinogenic amino acids fulfill various functions. Some arise as post-translational modifications in proteins (e.g. phosphotyrosine , hydroxyproline , formylmethionine , cystine , lanthionine , djenkolic acid , 2,6-diaminopimelic acid ). Others are metabolites in the metabolism (e.g. ornithine , citrulline , argininosuccinate , sarcosine , homoserine , homocysteine , L-DOPA , 5-hydroxytryptophan ). Others serve as hormones ( L - thyroxine ) and neurotransmitters (e.g. GABA , D - serine ) or as toxins ( β-methylamino-alanine , ibotenic acid , L - azetidine-2-carboxylic acid ).
Over 250 different non-proteinogenic amino acids have been found to be the building blocks of oligopeptides or short polypeptides, which are built up by non- ribosomal peptide synthetases from various types of archaea , bacteria , fungi and nudibranchs .
Artificially produced amino acids are z. B. the inhibitors isoserine , 2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid and the synthesis base for β-lactam antibiotics D- phenylglycine . In the Miller-Urey experiment , among other things, the amino acids norvaline and norleucine were artificially produced.
structure
In contrast to the proteinogenic amino acids, not all non-proteinogenic amino acids are L-α-amino acids, e.g. B. the group of D-amino acids or the non-α-amino acids such as β-alanine , GABA, δ-aminolevulinic acid or 4-aminobenzoic acid . Other non-proteinogenic amino acids have a modified peptide backbone such as 3-aminoisobutyric acid or dehydroalanine . There are also non-proteinogenic amino acids with two centers of chirality such as e.g. B. cystathionine , lanthionine, djenkolic acid or 2,6-diaminopimelic acid. Sulfur- containing non-proteinogenic amino acids are e.g. B. homocysteine , ethionine and felinine . Selenium- containing non-proteinogenic amino acids are methyl selenocysteine and selenomethionine .
| amino acid | function | structure | Structural formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taurine |

|
||
| L - thyroxine (T 4 ) | Hormone the thyroid | L-α-amino acid |
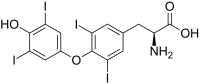
|
| 2,6-diaminopimelic acid (DAP) | Component in bacterial cell walls | α-amino acid with 2 stereocenters |
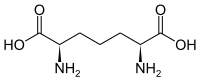
|
| Azetidine-2-carboxylic acid | Toxin of the lily of the valley | L-α-amino acid, secondary amine in a ring |

|
| Sarcosine | Metabolic intermediate in amino acid metabolism | N -methyl-α-amino acid |

|
| Homoser | Methionine breakdown product | L-α-amino acid |

|
| Lanthionine | in structural proteins | α-amino acid with 2 stereocenters |
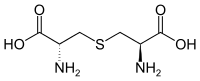
|
| Djenkolic acid | Food poison from Archidendron jiringa (Jengkol), a legume | α-amino acid with 2 stereocenters |

|
| Cystathionine | Intermediate in the biosynthesis of cysteine | α-amino acid with 2 stereocenters |

|
| L - homocysteine | Methionine breakdown product | L-α-amino acid |

|
| Ethionine | Methionine - Antagonist | L-α-amino acid |

|
| 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) | Preliminary stage of heme | δ-amino acid |

|
| p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) | bacterial folic acid synthesis | aromatic backbone |

|
| Dehydroalanine (DHA) | Cysteine breakdown product | Double bond on the α-C atom |

|
| γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) | inhibitory neurotransmitter | γ-amino acid |
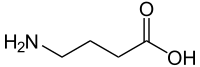
|
| 3-aminoisobutyric acid | is involved in lipid metabolism | β-amino acid |

|
| L - ornithine | Metabolic intermediate in the urea cycle | L-α-amino acid |

|
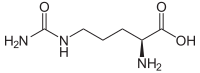
| L - citrulline | Metabolic intermediate in the urea cycle | L-α-amino acid |
|
| Argininosuccinate | Metabolic intermediate in the urea cycle | L-α-amino acid |

|
| L - 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine ( L -DOPA) | Metabolic intermediate in the synthesis of catecholamines | L-α-amino acid |

|
| L - 5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) | Metabolic intermediate in serotonin synthesis | L-α-amino acid |

|
| β-alanine | Building block of coenzyme A | β-amino acid |

|
| β-N-methylamino-alanine | Neurotoxin in cyanobacteria | L-α-amino acid |

|
| Ibotenic acid | Mushroom poison | L-α-amino acid |

|
| D - valine | Part of the antibiotic valinomycin | D-amino acid |
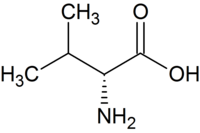
|
| D - alanine | Component in bacterial cell walls | D-amino acid |

|
| D - glutamic acid | Component in bacterial cell walls | D-amino acid |

|
| Hypoglycine | Akee plant toxin | L-α-amino acid |

|
| L -4- hydroxyproline | Stabilizes the structure of the collagen | L-α-amino acid, secondary amine in a ring |

|
| Pipecolic acid | Lysine breakdown product | L-α-amino acid, secondary amine in a ring |
Applications
Non-proteinogenic amino acids can be incorporated into proteins by non- ribosomal peptide synthetases , by protein ligation , by peptide synthesis or by genetic reprogramming. With peptides containing non-proteinogenic amino acids, the substrate specificities of peptidases can be investigated and protease inhibitors developed. β-peptides are made up of β-amino acids.
Individual evidence
- ^ Jan Koolman, Klaus Heinrich Roehm: Color Atlas of Biochemistry . 3rd edition, Thieme 2012. ISBN 978-3-13-169693-9 .
- ^ Gerhard Habermehl, Peter E. Hammann: Naturstoffchemie: An introduction . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-662-08929-3 ( Google Books ).
- ^ Peter Nuhn: Naturstoffchemie , S. Hirzel Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft Stuttgart 1990, ISBN 3-7776-0473-9 . P. 70.
- ↑ see entries monomers in the NORINE database .
- ↑ GH Hur, CR Vickery, MD Burkart: Explorations of catalytic domains in non-ribosomal peptide synthetase enzymology. In: Natural product reports. Volume 29, Number 10, October 2012, pp. 1074-1098, doi : 10.1039 / c2np20025b , PMID 22802156 .
- ^ U. Arnold: Incorporation of non-natural modules into proteins: structural features beyond the genetic code. In: Biotechnology letters. Volume 31, Number 8, August 2009, pp. 1129-1139, doi : 10.1007 / s10529-009-0002-9 , PMID 19404746 .
- ↑ A. Ohta, Y. Yamagishi, H. Suga: Synthesis of biopolymers using genetic code reprogramming. In: Current opinion in chemical biology. Volume 12, Number 2, April 2008, pp. 159-167, doi : 10.1016 / j.cbpa.2007.12.009 , PMID 18249198 .
- ^ Y. Lu, S. Freeland: On the evolution of the standard amino-acid alphabet. In: Genome biology. Volume 7, number 1, 2006, p. 102, doi : 10.1186 / gb-2006-7-1-102 , PMID 16515719 , PMC 1431706 (free full text).
- ↑ P. Kasperkiewicz, AD Gajda, M. Drąg: Current and prospective applications of non-proteinogenic amino acids in profiling of proteases substrate specificity. In: Biological chemistry. Volume 393, number 9, September 2012, pp. 843-851, doi : 10.1515 / hsz-2012-0167 , PMID 22944686 .


