Citrulline
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structural formula of L - (+) - citrulline, the naturally occurring enantiomer | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Citrulline | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 13 N 3 O 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white crystalline solid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 175.19 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
214 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
good in water (200 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
L - (+) - citrulline is a non- proteinogenic α- amino acid that is produced by plants and animals. Citrulline is named after the watermelon ( Citrullus vulgaris ) in which it is concentrated. Correspondingly, it also occurs in other cucurbits .
Citrulline is a homologue of L - homocitrulline , which is derived from L - lysine by carbamoylation .
Enantiomers
Citrulline has a stereocenter, so there are two chiral enantiomers .
Whenever the term "citrulline" is used in this article or in the scientific literature without any addition, it always means L - (+) - citrulline.
| Enantiomers of citrulline | ||
| Surname | L - (+) - citrulline | D - (-) - citrulline |
| other names | ( S ) -citrulline | ( R ) -citrulline |
| Structural formula | 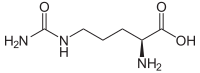 |

|
| CAS number | 372-75-8 | 13594-51-9 |
| 627-77-0 (racemate) | ||
| EC number | 206-759-6 | - |
| 211-012-2 (racemate) | ||
| ECHA info card | 100.006.145 | - |
| 100.010.012 (racemate) | ||
| PubChem | 9750 | 637599 |
| 833 (racemate) | ||
| DrugBank | DB00155 | - |
| - (racemate) | ||
| Wikidata | Q408641 | Q27077003 |
| Q27102910 (racemate) | ||
Occurrence
It is an intermediate product of the urea cycle . It normally arises from L - ornithine and carbamoyl phosphate, with its phosphate residue being split off by the ornithine carbamoyl transferase. It then reacts further with L - aspartate (anion of aspartic acid) to form L - argininosuccinate (enzyme: argininosuccinate synthetase) , splitting adenosine triphosphate . Aspartate is produced by transamination of oxaloacetate and introduces one of the two amino groups required for the urea produced into the urea cycle. The other is from carbamoyl phosphate.
physiology
Citrulline is increasingly excreted in the urine when people suffer from so-called nitrosative stress. Nitrosative stress is an endogenous exposure in the human body due to the nitrogen monoxide radical. In the urea cycle , arginine reacts more intensely with oxygen , producing NO and citrulline. Citrulline is therefore used as a marker for nitrosative stress in medical diagnostics .
Citrullination
As Citrullination the enzymatic conversion of arginine to citrulline is referred to. Peptidyl arginine deiminases (PAD) catalyze this post-translational modification , which takes place on certain proteins and peptides. These citrullinated proteins or peptides can be viewed by the immune system as foreign and, for example, attacked by antibodies . Citrullinated peptides, for example, play an important role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Data sheet L (+) - Citrulline from Acros, accessed on January 6, 2008.
- ↑ a b Data sheet L-Citrulline, ≥98% (TLC) from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 13, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ↑ M. Wada: About citrulline, a new amino acid in the pressed juice of watermelon, Citrullus vulgaris schrad. In: Biochem. Time. , 1930, 224 , pp. 420-429.
- ↑ G. Klein (editor, author) Handbuch der Pflanzenanalyse, fourth volume / first half, special analysis, third part, organic substances III - special methods - tables , 1933, 840 , pp. 61-62, Springer-Verlag, 2. July 2013
- ↑ External identifiers of or database links for L- homocitrulline : CAS number: 1190-49-4, EC number: 214-722-0 , ECHA InfoCard: 100.013.384 , PubChem : 65072 , ChemSpider : 58582 , Wikidata : Q18207833 .
- ↑ Bodo Kuklinski: Das HWS-Trauma , Aurum Verlag, 2006.
- ↑ P. Migliorini, F. Pratesi et al. a .: The immune response to citrullinated antigens in autoimmune diseases. In: Autoimmunity Reviews . Volume 4, Number 8, November 2005, pp. 561-564, doi : 10.1016 / j.autrev.2005.04.007 , PMID 16214096 (review).
- ^ R. Yamada, A. Suzuki et al. a .: Citrullinated proteins in rheumatoid arthritis. In: Frontiers in bioscience: a journal and virtual library. Volume 10, January 2005, pp. 54-64, PMID 15574347 (review).
- ↑ T. Gazitt, C. Lood, KB Elkon: Citrullination in Rheumatoid Arthritis-A Process Promoted by Neutrophil Lysis? In: Rambam Maimonides medical journal. Volume 7, number 4, October 2016, p., Doi : 10.5041 / RMMJ.10254 , PMID 27824546 , PMC 5101001 (free full text) (review).