Sarcosine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
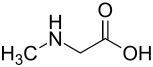
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Sarcosine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 7 NO 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, crystalline solid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 89.09 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
208 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
Decomposition: 212 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very good in water (1480 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−513.3 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Sarcosine (abbr .: Sar) is a non-proteinogenic amino acid . It is of glycine derived, an intermediate level of amino acid metabolism and a peptide component of the antibiotic actinomycin , the immunosuppressant cyclosporin and the angiotensin II - receptors - antagonists Saralasin . It is also found in muscles and other body tissues. Sarcosine also serves as a precursor for the preparation of certain surfactants (u. A. Acylsarcosines, z. B. lauroyl sarcosine and oleoyl sarcosine ), and is used in the printing of azo dyes .
Intramolecular rearrangement can result in alanine from sarcosine and glycine through demethylation .
history
Sarcosine was first isolated from the creatine of the meat broth by Justus von Liebig ( Greek σάρξ , sarx = meat), which is where the name comes from.
Medical relevance
While human urine usually does not contain sarcosine, it can be found in the urine of patients with prostate cancer . As a biomarker , it can therefore be used to diagnose prostate cancer. A distinction can be made between benign prostatic hyperplasia (benign enlargement of the prostate ) and metastatic and non-metastatic prostate cancer.
In addition, sarcosine at doses of 2 g per day in combination with other neuroleptics , with the exception of clozapine , reduced the typical symptoms of schizophrenia .
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on SARCOSINE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on March 4, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d Entry on sarcosine in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on June 6, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Data sheet Sarcosine at Acros, accessed on June 6, 2018.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-24.
- ^ K. Lindner: Tenside, textile auxiliaries, washing raw materials. Volumes I-III, Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft, Stuttgart 1964–1971.
- ^ A. Sreekumar, LM Poisson et al .: Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. In: Nature. Volume 457, Number 7231, February 2009, pp. 910-914. doi: 10.1038 / nature07762 . PMID 19212411 . PMC 2724746 (free full text).
- ↑ H. Lane, C. Huang, P. Wu, Y. Liu, Y. Chang, P. Lin, P. Chen, G. Tsai: Glycine transporter I inhibitor, N-methylglycine (sarcosine), added to clozapine for the treatment of schizophrenia . In: Biological Psychiatry . tape 60 , no. 6 , 2006, p. 645-649 , doi : 10.1016 / j.biopsych.2006.04.005 , PMID 16780811 .
- ↑ G. Tsai, H. Lane, P. Yang, M. Chong, N. Lange: Glycine transporter I inhibitor, N-methylglycine (sarcosine), added to antipsychotics for the treatment of schizophrenia . In: Biological Psychiatry . tape 55 , no. 5 , 2004, p. 452-456 , doi : 10.1016 / j.biopsych.2003.09.012 , PMID 15023571 .