Desmopressin
Desmopressin is a synthetic derivative of the body's own hormone vasopressin , which inhibits the excretion of urine. In contrast to vasopressin, desmopressin has a longer half-life and has less of an influence on blood pressure than natural vasopressin.
The active ingredient binds to certain receptors in the kidneys. As a result, the volume of urine and thus the number of toilet visits are significantly reduced.
| Desmopressin | ||
|---|---|---|

|
||
| Structural formula | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 9 amino acids, 1069 daltons | |
| Identifier | ||
| External IDs |
|
|
| Drug information | ||
| ATC code | H01 BA02 | |
| DrugBank | DB00035 | |
| Drug class | Antidiuretic | |
structure
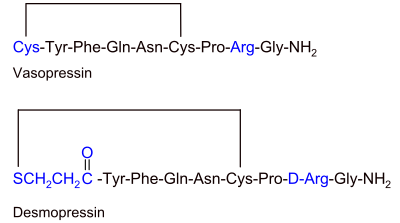
The primary structure of desmopressin (1-desamino-8- D- arginine-vasopressin; DDAVP) is derived from natural vasopressin. The modified peptide consists of 9 amino acids , with a deaminated N-terminal cysteine and a D - arginine instead of L -arginine at position 8 (see chirality (chemistry) ).
Mechanism of action
Desmopressin is a synthetic analogue of the body's own arginine vasopressin (AVP or ADH = antidiuretic hormone) and acts as an agonist of the AVP receptors in the kidneys. It differs from vasopressin, which is secreted from the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland, in receptor affinity. While AVP has a similar affinity to the V1 and V2 receptors, desmopressin, on the other hand, is significantly more affinity for the V2 receptor. Its binding affinity for the V1 receptor is even negligible. This plays an important role insofar as the binding to the V1 receptor results in an increase in blood pressure. Desmopressin therefore hardly affects blood pressure.
The V2 receptor, in turn, is mainly responsible for water retention in the collecting ducts of the kidney . If it is activated, it causes the installation of water channels ( aquaporins ) in the cell membranes, which allow water molecules to pass. As a result, the urine is dehydrated and thickened and thus more water is retained in the body.
There are also other effects of the V2 receptor: It triggers the release of the Von Willebrand factor and the expression of P-selectin during the exocytosis of the Weibel-Palade bodies of endothelial cells .
application
Desmopressin acts as an anti- diuretic . It inhibits the massive excretion of water that typically occurs in central diabetes insipidus . This significantly improves the quality of life of affected patients.
It is also approved for the treatment of traumatic polyuria and polydipsia , as well as for other diseases that are associated with an ADH deficiency, such as after surgery in the pituitary area or cranial brain injuries. It is also used as a diagnostic agent for the differential diagnosis of diabetes insipidus.
Another area of application is the treatment of nocturia in adults and nocturnal bed-wetting ( enuresis nocturna ) in children.
Desmopressin can also be given as an antihemorrhagic , e.g. B. in hemophilia , uremic thrombocytopathy , congenital and drug-induced platelet dysfunction or in Willebrand-Juergens syndrome .
Side effects
The more common side effects are generally pharmacodynamic related. Especially with increased fluid intake, there is increased water retention (desmopressin is a highly potent antidiuretic), which leads to an increase in volume with a relative lack of electrolytes. Warning signs for this are headache, nausea / vomiting and weight gain. In rare severe cases, it can lead to cerebral edema, sometimes combined with seizures or impaired consciousness.
Furthermore, there are seldom side effects such as allergies and cardiovascular problems (e.g. angina pectoris ) that accompany the rise in blood pressure.
Dosage forms
Desmopressin is one of the few medicines that offers nasal sprays in addition to tablets and orodispersible tablets . Due to its low molar mass , the hormone can easily enter the bloodstream through the nasal mucosa . However, the indication for nocturnal enuresis has been withdrawn for the nasal spray, as the tablet form has proven to be safer to use. The orodispersible tablet , which has also been approved in Germany since June 1, 2011 and has been sold in other countries for a long time, is intended to ensure safer absorption and effectiveness. Due to the better bioavailability, a lower exposure to active ingredients is possible with the same effect. Minirin is also available as an infusion solution for intravenous and subcutaneous administration.
Trade names
Adin (A), Desmogalen (D), Desmospray (D), Desmotabs (D), Minirin (D, A, CH), Nocdurna (D, A, CH), Nocutil (D, A, CH), Novidin (A ), Octostim (D, A, CH), various generics (D, A).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c K. Aktories among other things: General and special pharmacology and toxicology. 19th edition. Urban & Fischer, 2011, ISBN 978-3-437-42523-3 , p. 706.
- ↑ S. Kanwar, RC Woodman, MC Poon, T. Murohara, AM Lefer, KL Davenpeck, P. Kubes: Desmopressin induces endothelial P-selectin expression and leukocyte rolling in postcapillary venules . In: Blood . tape 86 , no. 7 , October 1, 1995, p. 2760-2766 , PMID 7545469 ( hematologylibrary.org ). Desmopressin induces endothelial P-selectin expression and leukocyte rolling in postcapillary venules ( Memento from December 14, 2007 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ JE Kaufmann, A. Oksche , CB Wollheim, G. Günther, W. Rosenthal, UM Vischer: Vasopressin-induced von Willebrand factor secretion from endothelial cells involves V2 receptors and cAMP . In: J. Clin. Invest. tape 106 , no. 1 , July 2000, p. 107–116 , doi : 10.1172 / JCI9516 , PMID 10880054 , PMC 314363 (free full text).
- ↑ a b Red List : 50.2.1.1. Desmospray 0.1 milligram / milliliter nasal spray solution (accessed April 18, 2012).
- ^ Friedman FM, Weiss, JP: Desmopressin in the treatment of nocturia: clinical evidence and experience . In: Ther Adv Urol . tape 6 , no. 5 , 2013, p. 310-317 , doi : 10.1177 / 1756287213502116 .
- ↑ D. Kaw, D. Malhotra: Platelet dysfunction and end-stage renal disease. In: Semin Dial. 19 (4), Jul-Aug 2006, pp. 317-322. Review. PMID 16893410
- ↑ Red List Online, as of August 2009.
- ↑ AM comp. d. Switzerland, as of August 2009.
- ↑ AGES-PharmMed, as of August 2009.