Famotidine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
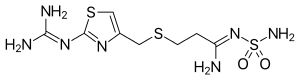
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Famotidine | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
3 - {[2- (diaminomethyleneamino) thiazol-4-yl] methylthio} - N '-sulfamoylpropanimidamide |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 15 N 7 O 2 S 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
Ulcer Therapeutics |
||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 337.4 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
6.9 |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Famotidine is a drug selected from the group of H 2 antihistamines , for the control of gastric acid production in the stomach ulcer - prophylaxis and for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease is used. In addition, famotidine is used in combination with drugs from the group of antacids to treat heartburn and acid regurgitation. The active ingredient was patented by Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical in 1980 .
Clinical information
Application areas (indications)
Famotidine is approved for the treatment of duodenal ulcers , benign gastric ulcers and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome , in which a reduction in gastric acid production makes sense. For the treatment of heartburn and acid regurgitation, famotidine is available in combination with antacids.
Contraindications (contraindications)
Famotidine is contraindicated in cases of known hypersensitivity to this active ingredient. There is insufficient experience in children, therefore famotidine should not be used in children as a precaution. Although the symptoms of malignant ulcers may respond to famotidine treatment, malignancy should be ruled out before starting treatment. Monotherapy with famotidine is not indicated if the gastrointestinal complaints are only minor.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Animal experiments on rats and rabbits did not give any indications of impairment of fertility or embryonic development. There is insufficient experience available for use in humans during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Famotidine can pass into breast milk.
Drug interactions
In the case of medicinal substances, the absorption of which depends on the pH of the stomach, the rate of absorption may be influenced by famotidine. Antacids, especially sucralfate , can decrease the absorption of famotidine. Probenecid delays the excretion of famotidine.
Adverse effects (side effects)
With a frequency of 1–10%, the most common side effects are headache , dizziness , constipation and diarrhea . Gastrointestinal complaints, including nausea , loss of appetite , vomiting and gas, can occasionally (0.1–1%) be observed. Occasional dry mouth , tiredness , rash and itching also occur. Other adverse drug reactions occur less frequently (<0.1%).
Pharmacological properties
Mechanism of action (pharmacodynamics)
Famotidine is an H 2 antihistamine and as such inhibits the gastric acid production-stimulating effect of the tissue hormone histamine at histamine H 2 receptors . Famotidine can suppress up to 90% of gastric acid production. The formation of pepsin is also inhibited and the volume of gastric juice formed is reduced.
Absorption and distribution in the body (pharmacokinetics)
The oral bioavailability of famotidine is 40–45%. Most of the famotidine is excreted unchanged in the urine. About 30-35% is oxidized to ineffective famotidine sulfoxide in the liver. Its elimination follows linear kinetics. The plasma half-life is 2.6 to 4 hours. The plasma half-life may be prolonged in patients with renal insufficiency . The protein binding is 15-20%.
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Shan-Yang Lin: An Overview of Famotidine Polymorphs: Solid-State Characteristics, Thermodynamics, Polymorphic Transformation and Quality Control in Pharm. Res. 31 (2014) 1619–1631, doi : 10.1007 / s11095-014-1323-5 .
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on famotidine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 1, 2019.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ a b c d e f Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices (BfArM): Sample text for specialist information: Famotidine tablets ( RTF ; 50 kB) Retrieved on November 5, 2011.
- ^ McNeil GmbH & Co. oHG: Specialist information Pepciddual chewable tablet. As of March 2009.
- ^ Campoli-Richards DM, Clissold SP: Famotidine. Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and a preliminary review of its therapeutic use in peptic ulcer disease and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome . In: Drugs . 32, No. 3, September 1986, pp. 197-221. PMID 2875864 .
- ^ Smith JL: Clinical pharmacology of famotidine . In: Digestion . 32, No. Suppl 1, 1985, pp. 15-23. PMID 2866132 .