Telecontrol
Under remote operation , the remote monitoring and control spatially distant objects by means of signal-converting method, of one or more locations from understood.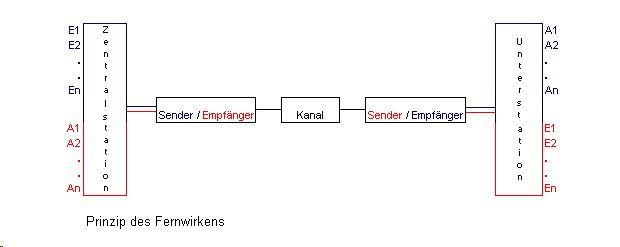
Special data transmission protocols are used to securely transmit the process data over wide area networks with low bandwidth and transmission quality.
Examples are:
- Remote control of operational and technical building systems such as heating , kitchen appliances , video recorders
- Monitoring and control of energy consumption ( gas meter , electricity meter - see also ripple control and radio ripple control technology )
- Control of supply networks ( electricity , gas , water , district heating ) as part of the network control system
- Control of road traffic systems: traffic lights , street lighting , de-icing agent spray systems
- Hazard notification ( burglary , fire )
- Emergency call
Telecontrol technology is divided into two areas. These are the telecontrol sub-stations (which are installed in the process or close to the process) and the telecontrol centers. The telecontrol centers (synonyms for this are process coupling systems, telecontrol gateways) are nowadays set up remotely from the process and are assigned to the control system components. Telecontrol substations and centers are linked to one another via WAN connections.
conditions
Such services are technically characterized by certain requirements for devices and transmission paths:
- low probability of failure
- low bit error rate
- fast data transfer
- special measures for security and data protection
Types of information
In telecontrol technology are transmitted
- Switching and positioning commands
- Switch position messages
- Identification and warning messages
- Readings
- Counts
- other data
Structure of a telecontrol device
A telecontrol device typically consists of one
- Numerous different process assemblies (interface between process and system bus. They adapt the signal level to the process conditions. Their function consists in the analog / digital conversion and the digital / analog conversion of information, but also in the summation of counting pulses.)
- the system bus
- the control unit / central unit
- the transmit / receive head, which forms the interface to the transmission technology.
If a telecontrol device is equipped with several send / receive heads, several remote stations can be operated. This can also be done using different telecontrol protocols.
There have been several attempts in the past to standardize the techniques for remote control. These attempts were initially unsuccessful. Due to the common specification of the IEC protocols by several manufacturers, a clear standardization is now emerging for new installations. Due to the relatively long service life of telecontrol systems, the service life of the protocols is around 10–20 years, so that many old protocols are still in use.
Currently you meet z. B. the following protocols:
- IEC 60870 with the user standards IEC 60870-5-101, IEC 60870-5-104 (current standard in Europe and Asia)
- IEC 61850 standard used worldwide for communication in switchgear and in the energy sector
- DNP3 .0 (US standard)
- FW535 / 537, SINAUT ( Siemens AG ),
- Modbus RTU ( AEG )
- Modnet-1F / SEAB-1F (formerly AEG, today OHP GmbH)
- TG 065, TG 709, TG 80x (formerly L&G, today Siemens AG )
- UNIP (SAE ELECTRONICS)
- DULZ / DULU ( IDS group )
- Ridat ( Rittmeyer AG )
- ReSyNet ( Phoenix Contact )
- HST TeleMatic, IP-based protocol according to DWA-M 207 (HST Systemtechnik GmbH)
- MFW-1G ( EES - Elektra-Elektronik GmbH & Co Störcontroller KG )
- ODP, Modbus -based protocol (Videc GmbH)
Product-dependent performance features are, for example:
- event-controlled data transmission
- Archiving based on time stamps
- Monitoring and visualization of the WAN connections
- automatic update after elimination of connection problems
Telecontrol systems use practically all telecommunications networks that enable data transmission , for example
- Leased lines (copper wires and fiber optics )
- AC telegraphy
- Private radio networks
- Analog telephone network via modem
- Digital ISDN network
- Cellular network ( GSM , 900 MHz and 1800 MHz, in Germany D-Netz and E-Netz , especially GPRS is used for this)
- Satellite communication
Telemetry and telematics have a similar area of responsibility ; therefore these terms are often used synonymously.
Further guidelines / recommendations
The BDEW (formerly VDEW ) were recommendations for remote control systems in utilities issued. These deal with the "planning and use of telecontrol systems" and the "technical conditions for telecontrol systems". There are also the following VDE regulations: VDE 0160, 0660, 0670, 0800 and 0804.
literature
- Lutz J. Heinrich, Armin Heinzl, Friedrich Roithmayr: Wirtschaftsinformatik-Lexikon. 7th edition. Oldenbourg-Verlag, Munich 2004, ISBN 3-486-27540-2 .
- Fritz Jörn: The telephone advisor. Franzis Verlag, Munich 1992, ISBN 3-7723-4751-7 .
- Heinrich-K. Podszeck: Carrier-frequency communications over high-voltage lines. 4th edition, Springer Verlag, Berlin / Heidelberg 1971, ISBN 978-3-662-10586-3 .
- Firoz Kaderali: Digital Communication Technology I. Networks - Services - Information theory - Coding, Friedrich Vieweg & Sohn Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Braunschweig 1991, ISBN 978-3-528-04710-8 .
- Detlef Jürgen Brauner, Robert Raible-Beste, Martin M. Weigert: Multimedia-Lexikon. R. Oldenbourg Verlag, Munich 1998, ISBN 3-486-24445-0 .
Web links
- IT knowledge remote control (accessed on September 4, 2017)
- Remote control of decentralized energy generation systems (accessed on September 4, 2017)
- Telecontrol and remote maintenance The future belongs to the web and cloud (accessed on September 4, 2017)
- Industrial data connections for remote maintenance and remote control in the GSM cellular network (accessed on September 4, 2017)