Spotted jewel beetle
| Spotted jewel beetle | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Females of the spotted jewel beetle |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Anthaxia fulgurans | ||||||||||||
| ( Cabinet , 1789) |
The spot-neck jewel beetle ( Anthaxia fulgurans ) is a beetle from the family of the jewel beetle . The species-rich genus Anthaxia is represented in Europe with four sub-genera. The spotted jewel beetle belongs to the subgenus Anthaxia , which has 46 species in Europe.
Like almost all species of jewel beetles, the spotted jewel beetle is particularly protected by the Federal Species Protection Ordinance . The beetle is considered to be critically endangered nationwide . In Saxony-Anhalt it is classified as extinct .
Notes on the name
The beetle (a female) was described by Cabinet in 1789 under the scientific name Buprestis fulgurans . The species name fúlgurans ( Latin for flashing, blinking) is not explicitly justified by cabinet. But it is self-explanatory by the description of the color of the closet (gold-green ... with fiery red wing-cover edges).
The genus Buprestis was broken down into many genera by Eschscholtz in 1829. The genus Anthaxia belongs to the genera with a pointed label . The genus name Anthaxia is from Altgr. άνθος ánthos, "blossom", and άξιος áxios, "worth" derived and indicates the most colorful species of this genus.
The German name Fleckhals-Prachtkäfer refers to the two black spots on the pronotum.
The beetle has been described several times, eleven synonyms are listed in the Fauna Europaea.
Characteristics of the beetle
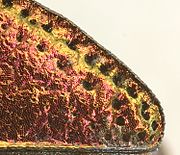
The beetle reaches a length of four to seven millimeters. It is one of the numerous small, colorful Anthaxia species that are flat (Fig. 2 above), wide and, conversely, boat-shaped. As is common in the genus, males and females are colored differently. The male (Fig. 1 below) is monochrome gold-green to green-blue. Both sexes have an extensive dark longitudinal spot on each side of the pronotum that extends for most of the length of the pronotum (Fig. 5). In the female (Fig. 1 above) the pronotum is darker blue-green, the wing covers are predominantly copper-red, near the base and along the front half of the wing cover seam they are blue-green to gold-green. They are also described as green with a copper-red border. The underside (Fig. 2 below) is green in both sexes. There are also completely blue specimens except for the black spots.
The head is drawn back into the pronotum up to the rear edge of the eyes, the mouthparts point diagonally downwards (Fig. 6). Between the eyes , the head is pressed flat lengthways and densely dotted . The eyes are large, oval and drawn closer together on the forehead. The short antennae have eleven links and are sawn from the 4th link. They are pivoted apart next to the front edge of the eyes. In contrast to many similar species, the forehead is hairless.
The pronotum (Fig. 5) is strongly rounded on the sides and wider than it is long. The pronotum base is almost straight, not double-curved. In the rear corners it is not only slightly but deeply indented (best visible in the taxi image). The impression extends over more than a third of the base width. The pronotum has a mesh structure. The meshes are along the middle of the pronotum, especially at the front, about the same width as they are long, rounded and each have a point in the middle. Against the sides, the stitches are lengthways and square.
The label (in Fig. 5 in the lower right corner) is small and triangular with rounded sides.
The wing covers cover the sides of the abdomen. Their sides run approximately parallel over the first two thirds, then they narrow slightly convex and end individually rounded. They are dotted in weakly developed rows and severely wrinkled (Fig. 7). Towards the apex of the elytra, the dots become noticeably coarse, the dots form rows along the edge of the elytra, disappearing towards the front (Fig. 4).
The underside of the body is shiny green and heavily dotted (Fig. 2 below). The legs are strong, the tarsi are all five-limbed, the claws are not toothed.
Figure 3 shows the aedeagus , which is also visible in the male in Figure 1.
biology
The larvae develop in various trees and shrubs that belong to the rose family , especially apple trees , as well as sloe , plum and bird cherry , probably also in hawthorn species and cornel cherry . They can be found in medium and small twigs, preferably in isolated, weakened trees on dry, warm locations. The larvae feed under the bark, the pupa cradle is placed in the wood. It takes a year or two to develop.
As a rule, the beetles are fully developed in autumn and overwinter in the pupa cradle. The beetles appear in spring, in South Tyrol the flight time begins in April, in Baden-Württemberg most beetles are found in May and June, the last finds are in early August. The beetles can be found on flowers of different plant families. Copulation takes place on the flowers.
distribution
The species is distributed from Asia Minor , Syria and the Ukraine in the east to the northeast of Spain . It is absent in North Africa and the range extends north to Poland . In Central Europe, the beetle was more widespread in warm areas in the south. Older literature speaks of finds around Geneva and in the Valais , in the Rhine valley around Colmar , Weilberg , Heidelberg , on the western slopes of the Vosges to Metz . Old finds are also known from Bavaria , Rhineland-Palatinate and Hesse . According to Fauna Europaea, however, the beetle does not occur in Switzerland. And in southern Germany, the only current finds come from the southern Upper Rhine, where the beetle is sometimes found frequently. Another find from Saxony from the period after 1950 is interesting because of its northern location. Only old finds are known from Saxony-Anhalt, the beetle is considered extinct there. Most of the finds come from a height of around 200 m. In southern France, however, the species occurs from sea level up to 1400 m high.
literature
- Heinz Joy, Karl Wilhelm Harde, Gustav Adolf Lohse: The beetles of Central Europe . tape 6 : Diversicornia . Spectrum, Heidelberg 1979, ISBN 3-87263-027-X , p. 226 .
- Klaus Koch : The Beetles of Central Europe Ecology . 1st edition. tape 2 . Goecke & Evers, Krefeld 1989, ISBN 3-87263-040-7 , pp. 97 .
- Fritz Brechtel, Hans Kostenbader (ed.): The splendor and stag beetles of Baden-Württemberg . Ulmer, Stuttgart (Hohenheim) 2002, ISBN 3-8001-3526-4 , p. 340 ff .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Anthaxia fulgurans at Fauna Europaea. Retrieved February 25, 2016
- ↑ Anthaxia at Fauna Europaea. Retrieved February 25, 2016
- ↑ Anthaxia (subgenus) in Fauna Europaea. Retrieved February 25, 2016
- ↑ Appendix 1 to the Federal Species Protection Ordinance
- ↑ Red list of jewel beetles in Saxony-Anhalt p. 297
- ^ F. Cabinet: Entomological observations in Johann Christian Daniel Schreber (Ed.): Der Naturforscher 24th piece, Halle 1789 p. 85
- ↑ Sigmund Schenkling: Explanation of the scientific beetle names (species)
- ↑ Johann-Friedrich Eschscholtz: Zoological Atlas…. 1st issue. Berlin 1829 p. 9 in the Google book search
- ↑ Sigmund Schenkling: Explanation of the scientific beetle names (genus)
- ↑ key Anthaxia at coleo-net
- ↑ Albert Huber: The warmth-loving animal world of the wider area around Basel in Archive for Natural History 22nd year, Department A, 7th issue, Berlin 1916 p. 58
- ↑ Distribution map of fulgurans in Europe according to FE ( Memento of the original from March 5, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.