Fleroxacin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
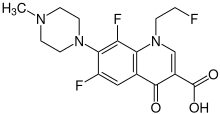
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Fleroxacin | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 17 H 18 F 3 N 3 O 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 369.34 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Fleroxacin is a drug from the group of quinolone antibiotics , more precisely the fluoroquinolone antibiotics . It was the first time in 1981 by Kyorin patented and is in the form of mono hydrochloride used. In Germany, the drug was on the market from 1995 to 2003 under the name Quinodis .
properties
The antimicrobial spectrum includes a number of gram-negative germs, including Enterobacteriaceae such as Klebsiella , E. coli , Salmonella , Shigella and Yersinia as well as Haemophilus and Neisseria , and Fleroxacin is also very effective against many staphylococci . It is less effective against Pseudomonas , but largely ineffective against streptococci and enterococci .
use
Fleroxacin is one of the fluoroquinolones with a wide range of indications. It can be administered either orally or parenterally, with a single dose usually being sufficient. It can be used to treat infections of the lower urinary tract, respiratory tract, and skin, among other things. Compared to other antibiotics, the use of Fleroxacin led to an increased incidence of undesirable effects after the market launch , which led to the drug being withdrawn from the market.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, the substance is rapidly and almost completely absorbed ; maximum plasma levels occur after 1 to 2 hours. The half-life is 10 to 12 hours, which is why a single dose per day is sufficient. Most of the excretion is renal , i.e. H. through the kidneys.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Fleroxacin data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 14, 2020 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on Fleroxacin. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 15, 2020.
- ^ The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals , 14th Edition (Merck & Co., Inc.), Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA, 2006, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 , pp. 700.
- ↑ U. Schwabe, D. Paffrath (Ed.): Drug Ordinance Report 2003 . Springer-Verlag, Berlin / Heidelberg 2004, p. 72 .
- ^ Medicines update. German STI Society (DSTIG), accessed on April 22, 2020 .
- ↑ a b K. Tobler: Fleroxacin . In: pharma criticism . tape 15 , no. 4 , 2004 ( infomed.ch [PDF]).
- ↑ Katrin Farker, Kurt G. Naber, Reinhard Fünfstück: Fluoroquinolones: Use in infections of the kidney and the urogenital tract . In: Medical Clinic , 2001, Vol. 96, No. 7, pp. 383-390, doi: 10.1007 / s00063-001-1063-2 .
- ↑ Winfried Kern: Quinolone Toxicity - New and Newly Reviewed . In: Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift , 2019, Volume 144, No. 24, pp. 1697–1702, doi: 10.1055 / a-0899-2883 .