GLUT-4
| GLUT-4 | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 509 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | multipass (12 TMS) membrane protein | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | SLC2A4 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Transporter classification | ||
| TCDB | 2.A.1.1 | |
| designation | Major facilitator superfamily / glucose transporter | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | Mammals | |
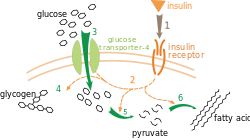
GLUT-4 (glucose transporter type 4) ( gene : SLC2A4 ) is a protein that is particularly in vesicles in mammalian - cells is localized. GLUT-4 is a membrane transport protein . In humans, GLUT-4 is expressed in striated muscle and fat cells. One of the consequences of the docking of insulin with the insulin receptor is that the GLUT-4 vesicles unite with the cell membrane and thus the smuggling of glucose into the cell is stimulated. Mutations in the GLUT4 gene can lead to GLUT-4 deficiency and this to a (rare) hereditary form of type 2 diabetes mellitus .
function
When the insulin level is low, the GLUT-4 vesicles slowly migrate to the endosomes and are broken down there. When the blood sugar level rises, the insulin level rises too. Insulin mediates the fusion of the vesicles with the plasma membrane. After the vesicles have been redirected to the outer membrane by insulin signal transduction , the glucose uptake of the cell can quickly increase to 20 to 50 times the value. The transporters are then resumed by endocytosis and can be used again. In the fat cells, the glucose can then be converted into triacylglycerols and stored in muscle cells in the form of glycogen . GLUT-4 is very similar to GLUT-1 , but cannot transport DHA.
regulation
The glucose uptake of muscle cells is regulated by the number of GLUT-4 molecules in the membrane and, at the same time, the frequency of their recycling via endocytosis. The activity of the transporter can also change. The number of GLUT-4 transporters is mainly increased by the effects of insulin. The recycling rate can be slowed down by muscle contraction, depolarization or a lack of energy. The activity is reduced when the enzymes glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase or hexokinase II bind to GLUT-4.
further reading
- Mohan SS, Perry JJ, Poulose N, Nair BG, Anilkumar G: Homology modeling of GLUT4, an insulin regulated facilitated glucose transporter and docking studies with ATP and its inhibitors . In: J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. . 26, No. 4, February 2009, pp. 455-64. PMID 19108584 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Orthologist at OMA
- ↑ UniProt P14672
- ↑ InterPro: IPR002441 Glucose transporter, type 4 (GLUT4)
- ↑ Clip A: The many ways to regulate glucose transporter 4 . In: Appl Physiol Nutr Metab . 34, No. 3, June 2009, pp. 481-7. doi : 10.1139 / h09-047 . PMID 19448718 .
- ↑ Antonescu CN, Foti M, Sauvonnet N, Klip A: Ready, set, internalize: mechanisms and regulation of GLUT4 endocytosis . In: Biosci. Rep. . 29, No. 1, February 2009, pp. 1-11. doi : 10.1042 / BSR20080105 . PMID 19143591 .
- ↑ Zaid H, Talior-Volodarsky I, Antonescu C, Liu Z, Klip A: GAPDH binds GLUT4 reciprocally to hexokinase-II and regulates glucose transport activity . In: Biochem. J. . 419, No. 2, April 2009, pp. 475-84. doi : 10.1042 / BJ20081319 . PMID 19140804 .