Grantha script
The Grantha script (from Sanskrit ग्रन्थ grantha "book" or "manuscript") belongs to the southern branch of Indian scripts . Like most Indian scripts, it is derived from the Brahmi script . The Grantha script can be proven epigraphically from the 6th century and was the predominant script in southern India for a long time. Today's Malayalam script is derived from the Grantha script and developed into an independent script in the 12th century. The development of the Tamil script was also strongly influenced by the Grantha script. Until the early 20th century, the Grantha script was the script in which Sanskrit was written in the Tamil areas of southern India ( Tamil Nadu ) and in Sri Lanka . It is still used in this function today.
Text examples
The Grantha text is Latin ( ISO 15919) and transliterated in Devanagari .
In June 2014, the font was included in the Unicode 7.0 standard as the Unicode block Grantha (U + 11300 – U + 1137F).
example 1
From the Kumarasambhavam of Kalidasa
अस्त्युत्तरस्यां दिशि देवतात्मा हिमालयो नाम नगाधिराजः। पूर्वापरौ तोयनिधी वगाह्य स्थितः पृथिव्या इव मानदण्डः॥
Example 2
Reproduction of the facsimile at the beginning of this article (John 3:16)
यत ईश्वरो जगतीत्थं प्रेम चकार यन्निजमेकजातं पुत्रं ददौ तस्मिन् विश्वासी सर्वमनुष्यो यथा न विनश्यानन्तं जीवनं लप्स्यते।
particularities
The Grantha script is an Abugida . It belongs to the Indian group of writings . For more information on the typology of Indian scripts and the alphabetical order, see Indian script group .
Grantha alphabet
Vowels
Consonants
Virama and vowel diacritics
Like other Abugidas , the consonant signs have the inherent vowel / a /. His absence is marked graphically with Virama (Halant):
For other vowels, vowel diacritics are used as follows:
Occasionally there are ligatures of consonants with vowel diacritics, e.g. B .:
Some consonants have special characters for the vowelless form:
Consonant ligatures
Grantha forms two types of consonant ligatures. The North Indian type is formed by fusing two or more consonants, analogous to most North Indian scripts such as B. Devanagari . In the South Indian type, the consonants are arranged one above the other, as in the scripts for Kannada and Telugu (and in some cases also Malayalam and the Indo-Aryan Oriya ).
North Indian type ligatures
South Indian type ligatures
Its components are easy to identify. Therefore only a few examples are given here:
Special forms for 〈ya〉 and 〈ra〉
![]() 〈Ya〉 and
〈Ya〉 and ![]() 〈ra〉 at the end of a consonant cluster become
〈ra〉 at the end of a consonant cluster become ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
![]() 〈Ra〉 at the beginning of a ligature is
〈Ra〉 at the beginning of a ligature is ![]() shifted to ("Reph") and, as in other Indian scripts, to the end of the spelling syllable (see Indian script circle ):
shifted to ("Reph") and, as in other Indian scripts, to the end of the spelling syllable (see Indian script circle ):
Grantha digits
The Grantha digits are identical to the old Tamil digits.
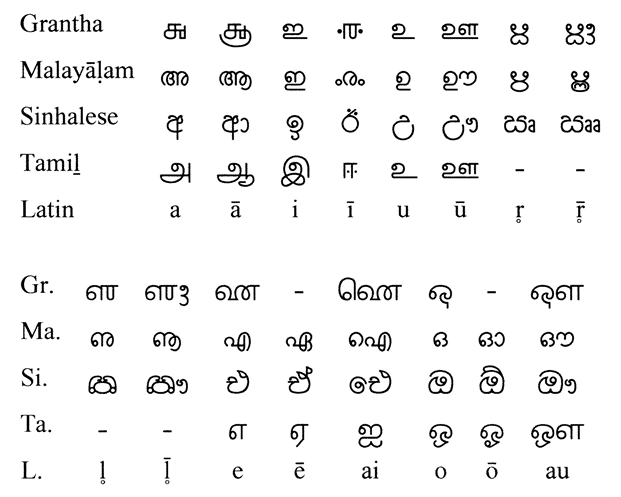
Comparison of Grantha with related writings
From the Grantha script, the scripts for Malayalam , Sinhala and Tamil have developed.
Vowels
Note: As in Devanagari , 〈e〉 and 〈o〉 stand for [eː] and [oː] in the Grantha script. Originally, Malayalam and Tamil did not differentiate between long and short 〈o〉 and 〈o〉, although both languages have the phonemes / e / / eː / and / o / / oː /. The introduction of additional characters for / eː / and / oː / goes back to the Italian missionary Constanzo Beschi (1680–1747).
Vowel diacritics
Consonants
The Tamil characters ஜ ஶ ஷ ஸ ஹ are also called "Grantha letters" because they were adopted from the Grantha script into the Tamil script to reproduce Sanskrit words . The characters ழ ற ன and the associated sounds appear only in Dravidian languages .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Unicode 7.0.0. Unicode Consortium, June 16, 2014, accessed June 17, 2014 .
literature
- Grantha script . In: Florian Coulmas: The Blackwell Encyclopedia of Writing Systems . Oxford: Blackwell Publishers, 1996. p. 173.
- Reinhold Grünendahl: South Indian Scripts in Sanskrit Manuscripts and Prints, Wiesbaden (Germany) 2001, ISBN 3-447-04504-3
- K. Venugopalan: A Primer in Grantha Characters http: // dsal.uchicago.edu/digbooks/dig_toc.html?BOOKID=PK419.V468_1983